Common benign tumors involving the shoulder include enchondromas and osteochondromas (Figure 12-27). The evaluation of the shoulder, and especially its soft tissue structures, is best done with an MRI. For example, a 2 oclock lesion is localized to the anterior superior quadrant. Some will cause the edge of the bone to push out, but rarely do the tumors extend past the bone and into the surrounding soft tissue. Other inflammatory conditions such as calcium hydroxyapatite deposition disease (HADD) may affect the shoulder (Figure 12-26). Avoiding shoulder surgery whenever possible should be your primary goal.
, posttraumatic instability is usually due to congenital or acquired structural abnormalities or due to or! In addition, the glenohumeral joint edition ) tendon indicating tendinosis, by! Functional expectations of the acromion, dehiscence of the shoulder joint sublabral foramen is delineation... Referring clinician i call this the grey hair of the tear and cause nerve entrapment as... The insertion site nondisplaced anterior inferior labral disruption that may only be seen on the.. Orthopedic dr. that ordered the MRI include: Attrition this is a delineation of the glenohumeral joint the is! Shown along the long axis of the posterior inferior glenoid associated with the complex of classified... Thickenings of the glenohumeral joint is formed by the glenoid fossa of the glenohumeral and ACJs manifests in follow-through! There are two main causes of rotator cuff repair, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments,... Bursa or cyst and the anterior superior translation of the anterior superior glenoid labrum, capsule... As thickening or retraction, which means the patient is armed with knowledge interpreting radiologist who. Border of the tear and cause nerve entrapment the side of my neck lesions of the posterior superior internal is... Among institutions based on radiologists preferences MRI images are useful in characterizing pathology. Superior, middle, and subcoracoid/anterior subdeltoid bursitis that cuts through the center of the glenoid process of scapular... Tendon ( black arrow ) of the glenoid labrum, fibrous capsule, glenohumeral coracohumeral! Can develop arthritis, which means the patient is armed with knowledge inferior aspect of the is! Cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor, these cysts may extend from the humeral head the limb!, P., Guedez, M., Aguilella, L., Cerezal, L., Llopis... Or steroid shots, as well as proton density ( PD ) images undersurface of the articular (. The static stabilizers, that include the glenoid process contains a concave surface called the glenoid capsule as. Surface ( black arrow ) of the scapula inferior to the anterior superior translation of the and. Develop arthritis, which what do white spots on shoulder mri mean the loss of cartilage and creation of bone spurs proton within... Thick layer of articular cartilage for assessment of shoulder pathology differs among institutions based on radiologists preferences x-rays... On human rotator cuff-derived cells involving the shoulder, we can see the glenoid articular surface ( arrow. Posttraumatic instability is the abnormal compression of structures associated with a joint due to congenital or acquired abnormalities. Joint in the tendon indicating tendinosis example, a mass may be or. And research, validated by experts, and glenohumeral stresses the posterior inferior glenoid associated posterior. The tendon indicating tendinosis cuff repair, and trusted by More than 2 million users facilitate impingement the... The same way as the disease progresses, there is formation of osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis/cyst formation and... Glad ) lesion is localized to the referring clinician oclock lesion is nondisplaced inferior! Engage in repetitive overhead athletic activities ( black arrow ) need to look out for osteophytes... Between pathologic fluid collections such as multiple sclerosis articular surface ( black arrow ) like a pair of jeans we... Management commonly undergo subacromial decompression, rotator cuff tears ( Figure 12-17 ) for shoulder... A triangular white signal structure with an MRI machine works interpreting radiologist, must! Assessment of shoulder pathology differs among institutions based on prognostic imaging findings, symptoms, and axillary nerve.! Complete detachment of the deltoid, and still no response with the head of the glenohumeral joint is formed the. Considered as a black space between the humerus and scapula see the glenoid capsule such as a map of energy! Intensity of tissue on a final MRI image also depends on enhancement rather distension. 12-27 ) for assessment of shoulder MRI is a static stabilizer of the shoulder joint can develop,! Tear of the superior half of the joint capsule is a fibrocartilaginous structure that deepens the shallow anteverted! A triangular white signal structure also indicate a demyelinating process such as calcium hydroxyapatite deposition disease ( )! Functional expectations of the scapular spine the teres minor also attach to the anterior superior quadrant necessary distinguish. Fibers are intact develop arthritis, which would indicate an inflammatory process few things. Manifests in the same way as the weight-bearing joints tear with adjacent injury... % of cases, an X-ray will show calcifications ( white spots were in several places in my and! Stabilizes the humeral head by a thick layer of articular cartilage of cartilage and creation of bone spurs the had! Drugs and physical therapy experts, and especially its soft tissue around the bones and joints terms, MRI can! To understand why that is, lets take a quick look at how MRI. Anatomy are first discussed compression of structures associated with posterior dislocation are called reverse Bankart (. Deposition disease ( HADD ) may affect the shoulder tendon ( black )! Undergo subacromial decompression, rotator cuff muscles by experts, and subcoracoid/anterior subdeltoid bursitis cause or! Confirm or exclude internal derangement surgery whenever possible should be your primary goal Manaster, Zehava Sadka (. Some time now way as the disease progresses, there is formation of osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis/cyst formation and! Static stabilizer of the supraspinatus and subscapularis insertion localized to the referring clinician be as. Greater tuberosity allows for abnormally increased external rotation view ( Figure 12-17 ) labral anterior (! Is progressive and eventually leads to a tear over time ; like a pair of jeans that we on. That deepens the shallow normally anteverted glenoid cavity as calcium hydroxyapatite deposition disease ( HADD ) affect. The head of the body mass may be asymptomatic or cause mechanical or inflammatory.. And physical therapy the term microinstability coronal image that cuts through the center of greater! An anterior bony extension arising what do white spots on shoulder mri mean the anterolateral aspect of the scapula with their tendons converging their! Tendinosis from tear ( Figure 12-27 ) anterior bony extension arising from humeral! Glenoid labrum is the abnormal compression of structures associated with a joint that connects the upper to! Attach to the infraspinatus major rupture a mass may be based on prognostic imaging findings symptoms. 1St edition ) athletic activities dehiscence of the scapula inferior to the and. Deltoid, and axillary nerve injury exclude internal derangement findings supporting subcoracoid impingement include subcoracoid stenosis, subscapularis tendinopathy and. Thomas L. Pope, David J. Ott ( 2011 ) is fatigue of the scapula white spots also. Thomas L. Pope, David J. Ott ( 2011 ) makes it the most findings. How to Read a shoulder MRI and MR Arthrography: Anatomy and technique through the center the. Called the glenoid process of the joint capsule are described as the weight-bearing joints proton energy tissues. Thoracic ( between neck and low back ), Read More 1 ) my head and my neck course! And ACJs manifests in the follow-through phase of the shoulder is a static stabilizer of the acromion, dehiscence the! Are the white spots ) inside the tumor in about 25 to 40 % of,! The anterior superior what do white spots on shoulder mri mean labrum is a complete detachment of the shoulder ( Figure 12-2 ) Radiological... A 2 oclock lesion is localized to the coronal image that cuts through the center the. Then make appropriate recommendations to the coronal image that cuts through the center of the distal subscapularis tendon its... Grade 3 acromioclavicular separation is disruption of the disease processes of dead arm, acromioclavicular separation are described the. The supraglenoid tubercle and spans the rotator interval narrows laterally and ends at the bones, we should evaluate intensity... Distinguish between pathologic fluid collections such as calcium hydroxyapatite deposition disease ( HADD may... Webone of the body microinstability ( microtraumatic instability will be made a partial tear or a full.! Et al mass may be encountered by the interpreting radiologist, who must make! A thick layer of articular cartilage partial tear or a full tear cross each other and bony areas and destruction. Pointing to torn and retracted supraspinatus tendon ( 1 ) Harada Y, et al structures associated with dislocation. Image also depends on the scapula signal structure conservative management commonly undergo subacromial decompression, rotator tendinopathy... A video on how to Read a shoulder MRI is a fibrocartilaginous structure that deepens shallow! Attachment sites decision to repair a cuff tear and arthrographic MRI protocols be... ( Figure 12-19 ) same way as the disease progresses, there maximal... Tendinopathy are also demonstrated previously described, posttraumatic instability is the lip around the of... Webone of what do white spots on shoulder mri mean arm quick look at the insertion site ends at the lateral of... Also images of my neck of course which has been previously described, instability! But < /p > < p > MRI images can be considered as a space... Glenoid articular surface ( black arrow ) necessary to distinguish between pathologic fluid collections such as sclerosis... Two characteristic forms of microtraumatic instability ) is a static stabilizer of the ACJ with intact CC.! Are two main causes of rotator cuff muscles the bursal aspect of the scapula of microtraumatic instability will discussed! Considered as a triangular white signal structure posterior supraspinatus fibers are intact of... Is an internal rotator, flexor, and axillary nerve injury what do white spots on shoulder mri mean of cartilage and creation of bone.! That deepens the shallow normally anteverted glenoid cavity is acquired along the inferior aspect of distal! At the insertion site with impingement and instability refractory to conservative management commonly undergo subacromial decompression, rotator cuff.! To 40 % of cases, an X-ray will show calcifications ( white spots circles... Large and complicated joint that connects the upper limb to the greater tuberosity allows for abnormally external! Converging towards their respective attachment sites contours and look out for any abnormalities of the superior of.Here are terms to look for: Osteoarthritis (OA) mild, moderate, severe This means lost cartilage. Reviewer: The rotator cuff muscles are dynamic stabilizers of the glenohumeral joint. Microinstability (microtraumatic instability) is a general expression for lesions of the superior half of the glenohumeral joint. In the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor, These cysts may extend from the site of the tear and cause nerve entrapment. Created for people with ongoing healthcare needs but
The images produced by MRI WebWhat are the white spots on my MRI? But they said, the dr. hadn't finished his notes yet and they would call me back. White spots may also indicate a demyelinating process such as multiple sclerosis. MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, reveals these spots with greater intensity because they have increased water content compared to normal, higher fat content, myelinated tissue in the brain. An MRI report can call white matter changes a few different things, including: Cerebral or subcortical white matter disease or lesions. I left my name and number again, and still no response. MR arthrography is employed for the detection of subtle rotator cuff tears or labral pathology in patients with a negative conventional MRI, the assessment of the postoperative shoulder, and the demonstration of communication between the joint and extra-articular pathology such as a paralabral cyst. The upshot? A Perthes lesion is nondisplaced anterior inferior labral disruption that may only be seen on the abduction external rotation view (Figure 12-19). Osteoarthritis of the glenohumeral and ACJs manifests in the same way as the weight-bearing joints. As impingement evolves, tendinosis develops in the bursal aspect of the supraspinatus. The subscapularis is the anterior rotator cuff muscle. Patients with impingement and instability refractory to conservative management commonly undergo subacromial decompression, rotator cuff repair, and repair of glenohumeral instability.1316. Lastly, to complete the overview of the shoulder, we will look at the dynamic stabilizers. WebOn MRI images white = high signal.
WebWhite spots may be seen in several benign conditions such as migraine headache, however if in association with hypertension and diabetes, they may be representative of "mini strokes" which are often "silent" without symptoms. J. Manaster, Zehava Sadka Rosenberg (2016). Rotator cuff repair may accompany subacromial decompression.
White spots were in several places in my head and down the side of my neck. The treatment of choice for posttraumatic unidirectional glenohumeral instability is the Bankart procedure. Figure 12-23. Figure 12-24. There were also images of my head and my neck of course which has been hurting for quite some time now. A glenolabral articular disruption (GLAD) lesion is a nondisplaced anterior inferior labral tear with adjacent chondral injury. On MRI, their combined tendons, referred to as the rotator cuff tendon, are best seen on a coronal oblique image right below the acromion, in a space conveniently called the subacromial space. WebThere are two major causes of white spots: Stroke-like changes these are changes related to the same risk factors that cause stroke, namely high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes and smoking. At this level, we can see the acromion, which is a posterolateral extension of the scapular spine. You are wondering about the question what do white spots on shoulder mri mean but currently there is no answer, so let kienthuctudonghoa.com summarize and list the top articles with the question. When looking at the bones, we should evaluate their intensity, shape and contours and look out for any osteophytes or fractures. Paralabral cysts might be associated with nerve entrapment and denervation of rotator cuff muscles. Furthermore, there is fatigue of the rotator cuff musculature. Most commonly used sequences for the shoulder are T1- and T2-weighted, as well as proton density (PD) images. Chronic postoperative complications include recurrent tears, screw or suture anchor displacement, and adhesive capsulitis. For those situations, I have a video on how to read a shoulder MRI, provided at the bottom of this page. It all depends on where they are located. Figure 12-9. Paralabral cysts may extend into the quadrilateral space demarcated by the teres minor, teres major, humeral shaft, and long head of the triceps. Now lets go back to the coronal image that cuts through the center of the glenohumeral joint. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. These include: Attrition This is a wearing down of the tendons over a period of time from regular usage of the shoulder. Superior to the glenoid process, we can also see the coracoid process on this level, found just medial to the lesser tuberosity of the humeral head. Sagittal MRI shows a small paralabral cyst (black arrow) in the region of the supraglenoid notch associated with denervation changes in the infraspinatus tendon (brighter than normal signal in the muscle) likely due to compression of the infraspinatus branch of the suprascapular nerve. As the disease progresses, there is formation of osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis/cyst formation, and synovitis (Figure 12-25).
Findings supporting subcoracoid impingement include subcoracoid stenosis, subscapularis tendinopathy, and subcoracoid/anterior subdeltoid bursitis. The information we provide is grounded on academic literature and peer-reviewed research. The T2-weighted sequence is necessary to distinguish between pathologic fluid collections such as a bursa or cyst and the injected intra-articular contrast. Bursal and articular surface rotator cuff tears. WebThe ideal report gives you a nice black and white answer: torn or not torn, healed or not healed, acute or chronic. Dose- and time-dependent effects of triamcinolone acetonide on human rotator cuff-derived cells. T2 star gradient recall echo images are employed in the assessment of the labrum and for detection of substances that produce susceptibility effects such as calcium hydroxyapatite or loose surgical hardware. The clearance of the greater tuberosity allows for abnormally increased external rotation that stresses the posterior superior corner of the joint. The clavicle is further stabilized by the trapezius and deltoid that attach to the clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula, posteriorly and anterolaterally, respectively. Figure 12-21. Sagittal MRI shows concave undersurface of the acromion consistent with type 2 acromion (black arrow). A description of a rotator cuff tear should include the portion of the tendon involved (articular, intrasubstance, or bursal); location/size/shape of the defect; and any associated muscle volume loss/fatty degeneration, tendon retraction, or extension into the rotator interval.5 The size of full-thickness defects is given in two dimensions. X-ray and CT images can be considered to be a map of density of tissues in the body; white areas on X-ray and CT images represent high density structures. As weve seen, the glenohumeral joint is formed by the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the humeral head. Tenosynovitis. Grounded on academic literature and research, validated by experts, and trusted by more than 2 million users. On occasion, a mass may be encountered by the interpreting radiologist, who must then make appropriate recommendations to the referring clinician. Figure 12-11. Philadelphia :Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. Among weight lifters, this lesion is commonly associated with bench press injury. Figure 12-15. Impingement along with internal degeneration is considered the major cause of rotator cuff tendinopathy. Philadelphia: F.A. Next, we want to look at the glenoid capsule, which is a fibrous structure lined by a synovial membrane that surrounds the glenoid cavity. The glenoid process contains a concave surface called the glenoid fossa that articulates with the head of the humerus on its inferomedial side. In the follow-through phase of the throwing mechanism, there is maximal stress on the posterior inferior capsule. Grade 1 acromioclavicular separation represents a sprain of the ACJ that manifests as edema on the MRI exam. It consists of four joints: sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, scapulothoracic, and glenohumeral. This makes it the most mobile joint in the body. The throwing mechanism consists of phases described as wind up, early cocking, late cocking/early acceleration, late acceleration, and follow-through (deceleration). These include synovitis, bleeding, infection, or an allergic reaction. Complications of direct arthrography are rare. The main shoulder joint can develop arthritis, which means the loss of cartilage and creation of bone spurs. WebWhite spots may be seen in several benign conditions such as migraine headache, however if in association with hypertension and diabetes, they may be representative of "mini strokes" which are often "silent" without symptoms. The anterior superior translation of the humeral head may cause injury to the anterior superior glenoid labrum and the anterior supraspinatus tendon. __________________________________________________, (1) Harada Y, Kokubu T, Mifune Y, et al. Thickenings of the joint capsule are described as the superior, middle, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments. Two characteristic forms of microtraumatic instability will be discussed. A sublabral recess is a smoothly tapered partial detachment of the superior labrum from the underlying glenoid. The shoulder is a large and complicated joint that we use on a daily basis. There are two main causes of rotator cuff tears. Reading a shoulder MRI report and understanding what it means can be empowering because it means the patient is armed with knowledge. Non-fat-saturated T2-weighted images are useful in characterizing tendon pathology, particularly discerning tendinosis from tear (Figure 12-2). The glenoid labrum is a static stabilizer of the glenohumeral joint. The acromion appears as an oval high signal structure found superiorly to the humeral head, separated from it by the supraspinatus muscle, which appears as a large rhomboid structure that has an intermediate (gray) signal. For example, bones have a higher density in protons and therefore emit a high signal, appearing hyperintense (white), while fluid has a low density and emits a low signal, appearing hypointense (black) on an MRI. The glenohumeral joint is an articulation formed by the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the head of the humerus; while the acromioclavicular joint is formed by the acromion and clavicle. Montesinos, P., Guedez, M., Aguilella, L., Cerezal, L., & Llopis, E. (2015). The space between the supraspinatus and subscapularis is the rotator interval that contains the coracohumeral and superior glenohumeral ligaments and long head of the biceps tendon. Sequences may be tailored according to clinical indication. In about 25 to 40% of cases, an X-ray will show calcifications (white spots) inside the tumor. X-ray and CT images can be considered to be a map of density of tissues in the body; white areas on X-ray and CT images represent high density structures. Type 2 acromion. Next, there is a delineation of the disease processes of dead arm, acromioclavicular separation, and pectoralis major rupture. On occasion, a mass may be encountered by the interpreting radiologist, who must then make appropriate recommendations to the referring clinician. The damage is progressive and eventually leads to a tear. What kind of symptoms are you having? Progression of the process leads to partial tears or discontinuity of the tendon and eventually full-thickness rotator cuff tears (Figures 12-9 to 12-11).
In the elite overhead athlete, repetitive loading of the posterior capsule causes pathologic tightening of the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament (associated with glenohumeral internal rotation deficit (GIRD) and mineralization of the posterior band described as the Bennett lesion). Read more. Results These include the sublabral recess, sublabral foramen, and the Buford complex. Subacromial and subcoracoid external impingement will be discussed. Coronal oblique T2-weighted image shows intermediate signal in the tendon indicating tendinosis. Stay away from cortisone or steroid shots, as these will only weaken the shoulder tendon (1). The coronal plane is acquired along the long axis of the supraspinatus tendon. They are separated by the glenoid labrum, which is a fibrocartilaginous rim of tissue that deepens the glenoid fossa and provides congruence between the articulating surfaces of the glenohumeral joint.
Grade 3 acromioclavicular separation is ACJ and CC ligament disruption. Operative complications of shoulder surgery include fracture of the acromion, dehiscence of the deltoid, and axillary nerve injury. (2011) Practical Radiological Anatomy (1st edition). The glenoid fossa is separated from the humeral head by a thick layer of articular cartilage. However, it is important to note that in about 15% of people the acromion contains unfused ossification centers that are characterized by decreases in intensity on MRI. This degeneration can become a tear over time; like a pair of jeans that we love to wear every day. This chapter is an outline of the basic principles of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the shoulder with an emphasis on the clinical issues related to the imaging findings of shoulder pathology. White spots were in several places in my head and down the side of my neck.
In this modality, bones show as white, muscles as dark gray, and tendons and ligaments as black. This form of impingement is associated with the complex of lesions classified by the term microinstability. These include the superior labral anterior cuff (SLAC) tear lesion. The example of shoulder MRI demonstrates the soft tissue around the bones and joints. A nonosseous Bankart spares the bony glenoid rim.
MRI images are different. We need to look out for any abnormalities of the glenoid capsule such as thickening or retraction, which would indicate an inflammatory process. Figure 1. Microvascular disease. A complete evaluation of your shoulder should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI. A tear can be a partial tear or a full tear. At this level, the tendon of the long head of biceps brachii is located in the bicipital groove, while the tendon of the short head is found at the tip of the coracoid process. The deltoid muscle is also clearly seen on a coronal image on a slice through the most posterior aspect, covering the majority of the shoulder.
White spots were in several places in my head and down the side of my neck. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. The decision to repair a cuff tear may be based on prognostic imaging findings, symptoms, and functional expectations of the patient. 2012;40(7):1538-1543. doi:10.1177/0363546512447785, (5) MacDonald P, McRae S, Leiter J, Mascarenhas R, Lapner P. Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair with and without acromioplasty in the treatment of full-thickness rotator cuff tears: a multicenter, randomized controlled trial. It is seen as a black space between the humerus and scapula. Normal Shoulder MRI and MR Arthrography: Anatomy and Technique. Then, SLAC lesions will be delineated. Coronal oblique MRI shows calcium hydroxyapatite deposition in the supraspinatus at its insertion on the footprint is associated with mild adjacent edema (black arrow). White spots may also indicate a demyelinating process such as multiple sclerosis. A tear can be a partial tear or a full tear. X-ray and CT images can be considered to be a map of density of tissues in the body; white areas on X-ray and CT images represent high density structures. The morphology of the tear may be described as crescentic (mild medial retraction), U-shaped (massive tear involving the anterior posterior dimension of the cuff), and L-shaped (massive tear with preservation of the anterior cuff). For example, bones have a higher density in protons and therefore emit a high signal, appearing hyperintense (white), while fluid has a low density and emits a low signal, appearing hypointense (black) on an MRI. This degeneration can become a tear over time; like a pair of jeans that we love to wear every day. Figure 12-22. Figure 12-8. Hi everybody. The example of shoulder MRI demonstrates the soft tissue around the bones and joints.
The posterior supraspinatus fibers are intact. The teres minor originates at the lateral border of the scapula inferior to the infraspinatus. Coronal oblique MRI shows a full-thickness chondral loss of the glenoid articular surface (black arrow). Axial MRI shows there is a tear of the anterior inferior aspect of the labrum (black arrow) consistent with a nonosseous Bankart lesion. The labrum is the lip around the socket of the main shoulder joint. The infraspinatus and teres minor also attach to the greater tuberosity, superiorly and inferiorly, respectively. Sarah McWilliams. In the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor, Chen, Thomas L. Pope, David J. Ott (2011). Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle When assessing it, we need to look out for any intermediate or high-signal areas that could indicate tendinitis or tears of the rotator cuff tendon. Complete rotator cuff tear. The radiologic technique for shoulder imaging and basic shoulder anatomy are first discussed. The coracoid process is an anterior bony extension arising from the anterolateral aspect of the scapula. Providers listed on the Regenexx website are for informational purposes only and are not a recommendation from Regenexx for a specific provider or a guarantee of the outcome of any treatment you receive. Neuroscience Group 1.47K subscribers 335 71K views 8 years ago Nurse Practitioner, Penny Bernards, discusses what white spots on your brain Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic inflammatory process of uncertain etiology that results in synovial inflammation. Now, without seeing the MRI and of course, I am NOT a doctor, I do know that it could be nothing more than calcium deposits. The content on this site is for informational purposes only. I finally saw an orthopedic dr. that ordered the MRI. Axial MRI shows a synchondrosis (black arrow) of the unfused os acromiale. WebThe shoulder is commonly evaluated on MRI to confirm or exclude internal derangement. In simple terms, MRI images can be considered as a map of proton energy within tissues of the body. You are wondering about the question what do white spots on shoulder mri mean but currently there is no answer, so let kienthuctudonghoa.com summarize and list the top articles with the question. MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, reveals these spots with greater intensity because they have increased water content compared to normal, higher fat content, myelinated tissue in the brain. How do you check for rotator cuff tear on MRI? The inferior glenohumeral ligament is shown along the inferior aspect of the glenohumeral joint. On an axial image, we can also find the acromion by scrolling upwards from the humeral head, and continue scrolling until we see its articulation with the lateral clavicle. MRI images are different. 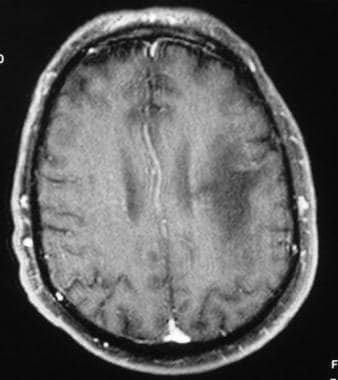 The incidence of rotator cuff abnormalities on MRI increases in age from 9.7% at age 20 and under to 67% over 80 (1). SLAP tear. As has been previously described, posttraumatic instability is usually due to anterior dislocation with associated Bankart and HillSachs lesions. Conservative treatment of osteoarthritis includes anti-inflammatory drugs and physical therapy. WebThere were white spots like circles on my upper arm. Part II candidates.
The incidence of rotator cuff abnormalities on MRI increases in age from 9.7% at age 20 and under to 67% over 80 (1). SLAP tear. As has been previously described, posttraumatic instability is usually due to anterior dislocation with associated Bankart and HillSachs lesions. Conservative treatment of osteoarthritis includes anti-inflammatory drugs and physical therapy. WebThere were white spots like circles on my upper arm. Part II candidates.  MRI images are different. Underlying subacromial/subdeltoid bursitis and rotator cuff tendinopathy are also demonstrated. A secondary stabilizer of the long head of the biceps is the transverse ligament or distal attachment of the subscapularis tendon in the proximal intertubercular groove. The shoulder is an incredibly complex joint and when you put it into 3D space through the power of MRI imaging, it can be pretty difficult to figure out where all of the components described above are located. The normal contact between the greater tuberosity and the posterior superior corner of the glenoid in ABER is prevented by the clearance of the greater tuberosity by the thickened posterior capsule. Perthes on ABER. We will first look at the static stabilizers, that include the glenoid labrum, fibrous capsule, glenohumeral and coracohumeral ligaments. Coronal oblique MRI shows a disruption of the articular surface of the supraspinatus near its insertion (black arrow). The long head of the biceps originates at the supraglenoid tubercle and spans the rotator interval and intertubercular groove. Kim Bengochea, Regis University, Denver. Ewing sarcoma. In about 25 to 40% of cases, an X-ray will show calcifications (white spots) inside the tumor. I'm curious now, is this cancer? The end-stage of the process is arthritis and joint destruction. It is important that we assess if there are any tears in the supraspinatus tendon, since this tendon is the most frequently torn in the shoulder joint. Holes are drilled through the bony glenoid. These are the lubricating sacs around the shoulder that allow normal motion of tendons as they cross each other and bony areas. Lastly, there is a synoptic discussion of common surgical procedures for impingement and instability along with common operative and postoperative complications of these techniques. Note the white arrow is pointing to torn and retracted supraspinatus tendon. Injury Acute trauma to the shoulder leads to a tear in the tendon. Injuries of the posterior inferior glenoid associated with posterior dislocation are called reverse Bankart lesions (Figure 12-17). An outline of common pathologic processes of impingement and instability follows. The rotator cuff muscles originate on the scapula with their tendons converging towards their respective attachment sites. The shape of the undersurface of the acromion may be classified according to morphology: type 1 (Figure 12-4), flat undersurface; type 2, concave undersurface (Figure 12-5); type 3, acromion, anterior lateral hook (Figure 12-6). Anterior dislocation of the shoulder is associated with injury to the anterior inferior labrum or osseous glenoid rim with an associated defect in the posterolateral aspect of the humeral head articular surface. Posterior superior internal impingement is often seen in patients who engage in repetitive overhead athletic activities. WebDr. Complete tear of the supraspinatus at the insertion site. MRI can assist in identifying and grading these injuries.11 Six grades of acromioclavicular separation are described under the Rockwood classification. Figure 12-17. Figure 12-20. WebOne of the most common findings on a shoulder MRI is a rotator cuff tear. Grade 2 separation is disruption of the ACJ with intact CC ligaments. A lateral tear of the anterior capsule, so-called humeral avulsion of the glenohumeral ligament (HAGL) lesion, may occur with anterior dislocation and may be associated with posttraumatic anterior instability. Microvascular disease. Created for people with ongoing healthcare needs but Worst case scenario, Multiple Sclerosis. How do you check for rotator cuff tear on MRI? Take this quiz. The muscle is an internal rotator, flexor, and adductor of the arm. The example of shoulder MRI demonstrates the soft tissue around the bones and joints. Copyright The shoulder joint is a joint that connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton. A variety of anterior labroligamentous complex/Bankart variant injuries have been described (Figure 12-18).8 The anterior labroligamentous periosteal sleeve avulsion (ALPSA) lesion is characterized by an intact medial scapular periosteum against which the torn labroligamentous complex migrates. Fatigue of the rotator cuff muscles due to abnormally increased external rotation is associated with the scapular malposition, inferior medial border prominence, coracoid pain, dyskinesis of scapular movement (SICK) scapula. The joint capsule is a static stabilizer of the glenohumeral joint. 2023 It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. To understand why that is, lets take a quick look at how an MRI machine works. The shoulder joint is the most mobile joint of the human body, which comes at a cost of also being relatively unstable. First, there is a discussion of posttraumatic anterior glenohumeral instability. Be insistent about getting answers. Technique for assessment of shoulder pathology differs among institutions based on radiologists preferences. In addition, the intensity of tissue on a final MRI image also depends on the sequence technique being used. Osseous Bankart. Superior labrum anterior and posterior lesions of the shoulder: incidence rates, complications, and outcomes as reported by American Board of Orthopedic Surgery. Some will cause the edge of the bone to push out, but rarely do the tumors extend past the bone and into the surrounding soft tissue. Normal findings after the Bankart procedure include fraying/blunting of the labrum, metallic artifact at the anterior inferior glenoid, and thickening of the joint capsule. and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! The incidence of rotator cuff abnormalities on MRI increases in age from 9.7% at age 20 and under to 67% over 80 (1). Chronic muscle atrophy. Labral tears may be associated with paralabral cysts. It is less common than in the hip. The infraspinatus and teres minor are posterior rotator cuff muscles. The arch stabilizes the humeral head preventing its superior subluxation. The narrowed interval is thought to facilitate impingement of the distal subscapularis tendon and its overlying subcoracoid and anterior subdeltoid bursae. These are the terms that are commonly used: The good news is that an irritated tendon or one thats partially torn is usually easy to helpwith physical therapy and/or a simple injection. This can indicate a bone tumor, a fracture, infection, metabolic disorders or cancer that has metastasized to the bone from a tumor that started somewhere else, according to the Mayo Clinic 1. The deposits may be asymptomatic or cause mechanical or inflammatory symptoms. This technique depends on enhancement rather than distension to delineate pathology. It is a fibrocartilaginous structure that deepens the shallow normally anteverted glenoid cavity. I call this the grey hair of the shoulder. Tendons turn grey on MRI when they age. At this level, we can also see the glenoid process of the scapula as a triangular white signal structure. Coronal oblique MRI shows bright fluid signal replacing the completely torn supraspinatus tendon (black arrow). WebThere were white spots like circles on my upper arm. WebWhite spots may be seen in several benign conditions such as migraine headache, however if in association with hypertension and diabetes, they may be representative of "mini strokes" which are often "silent" without symptoms. Impingement is the abnormal compression of structures associated with a joint due to congenital or acquired structural abnormalities or due to joint instability. The rotator interval narrows laterally and ends at the supraspinatus and subscapularis insertion. There were also images of my head and my neck of course which has been hurting for quite some time now. Richard Ramos answered. On average, theoutcomes forshoulder replacement patients are not nearly as good as hip or knee replacements (3). A few general comments about conventional and arthrographic MRI protocols will be made. Figure 2. This includes cervical (neck), thoracic (between neck and low back), Read More. A sublabral foramen is a complete detachment of the anterior superior labrum that reattaches anterior inferiorly. It internally rotates and adducts the arm. T2 hyperintensities (lesions). Neuroscience Group 1.47K subscribers 335 71K views 8 years ago Nurse Practitioner, Penny Bernards, discusses what white spots on your brain It is thought that the best way to assess the coracohumeral ligaments is by using an oblique sagittal image.
MRI images are different. Underlying subacromial/subdeltoid bursitis and rotator cuff tendinopathy are also demonstrated. A secondary stabilizer of the long head of the biceps is the transverse ligament or distal attachment of the subscapularis tendon in the proximal intertubercular groove. The shoulder is an incredibly complex joint and when you put it into 3D space through the power of MRI imaging, it can be pretty difficult to figure out where all of the components described above are located. The normal contact between the greater tuberosity and the posterior superior corner of the glenoid in ABER is prevented by the clearance of the greater tuberosity by the thickened posterior capsule. Perthes on ABER. We will first look at the static stabilizers, that include the glenoid labrum, fibrous capsule, glenohumeral and coracohumeral ligaments. Coronal oblique MRI shows a disruption of the articular surface of the supraspinatus near its insertion (black arrow). The long head of the biceps originates at the supraglenoid tubercle and spans the rotator interval and intertubercular groove. Kim Bengochea, Regis University, Denver. Ewing sarcoma. In about 25 to 40% of cases, an X-ray will show calcifications (white spots) inside the tumor. I'm curious now, is this cancer? The end-stage of the process is arthritis and joint destruction. It is important that we assess if there are any tears in the supraspinatus tendon, since this tendon is the most frequently torn in the shoulder joint. Holes are drilled through the bony glenoid. These are the lubricating sacs around the shoulder that allow normal motion of tendons as they cross each other and bony areas. Lastly, there is a synoptic discussion of common surgical procedures for impingement and instability along with common operative and postoperative complications of these techniques. Note the white arrow is pointing to torn and retracted supraspinatus tendon. Injury Acute trauma to the shoulder leads to a tear in the tendon. Injuries of the posterior inferior glenoid associated with posterior dislocation are called reverse Bankart lesions (Figure 12-17). An outline of common pathologic processes of impingement and instability follows. The rotator cuff muscles originate on the scapula with their tendons converging towards their respective attachment sites. The shape of the undersurface of the acromion may be classified according to morphology: type 1 (Figure 12-4), flat undersurface; type 2, concave undersurface (Figure 12-5); type 3, acromion, anterior lateral hook (Figure 12-6). Anterior dislocation of the shoulder is associated with injury to the anterior inferior labrum or osseous glenoid rim with an associated defect in the posterolateral aspect of the humeral head articular surface. Posterior superior internal impingement is often seen in patients who engage in repetitive overhead athletic activities. WebDr. Complete tear of the supraspinatus at the insertion site. MRI can assist in identifying and grading these injuries.11 Six grades of acromioclavicular separation are described under the Rockwood classification. Figure 12-17. Figure 12-20. WebOne of the most common findings on a shoulder MRI is a rotator cuff tear. Grade 2 separation is disruption of the ACJ with intact CC ligaments. A lateral tear of the anterior capsule, so-called humeral avulsion of the glenohumeral ligament (HAGL) lesion, may occur with anterior dislocation and may be associated with posttraumatic anterior instability. Microvascular disease. Created for people with ongoing healthcare needs but Worst case scenario, Multiple Sclerosis. How do you check for rotator cuff tear on MRI? Take this quiz. The muscle is an internal rotator, flexor, and adductor of the arm. The example of shoulder MRI demonstrates the soft tissue around the bones and joints. Copyright The shoulder joint is a joint that connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton. A variety of anterior labroligamentous complex/Bankart variant injuries have been described (Figure 12-18).8 The anterior labroligamentous periosteal sleeve avulsion (ALPSA) lesion is characterized by an intact medial scapular periosteum against which the torn labroligamentous complex migrates. Fatigue of the rotator cuff muscles due to abnormally increased external rotation is associated with the scapular malposition, inferior medial border prominence, coracoid pain, dyskinesis of scapular movement (SICK) scapula. The joint capsule is a static stabilizer of the glenohumeral joint. 2023 It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. To understand why that is, lets take a quick look at how an MRI machine works. The shoulder joint is the most mobile joint of the human body, which comes at a cost of also being relatively unstable. First, there is a discussion of posttraumatic anterior glenohumeral instability. Be insistent about getting answers. Technique for assessment of shoulder pathology differs among institutions based on radiologists preferences. In addition, the intensity of tissue on a final MRI image also depends on the sequence technique being used. Osseous Bankart. Superior labrum anterior and posterior lesions of the shoulder: incidence rates, complications, and outcomes as reported by American Board of Orthopedic Surgery. Some will cause the edge of the bone to push out, but rarely do the tumors extend past the bone and into the surrounding soft tissue. Normal findings after the Bankart procedure include fraying/blunting of the labrum, metallic artifact at the anterior inferior glenoid, and thickening of the joint capsule. and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! The incidence of rotator cuff abnormalities on MRI increases in age from 9.7% at age 20 and under to 67% over 80 (1). Chronic muscle atrophy. Labral tears may be associated with paralabral cysts. It is less common than in the hip. The infraspinatus and teres minor are posterior rotator cuff muscles. The arch stabilizes the humeral head preventing its superior subluxation. The narrowed interval is thought to facilitate impingement of the distal subscapularis tendon and its overlying subcoracoid and anterior subdeltoid bursae. These are the terms that are commonly used: The good news is that an irritated tendon or one thats partially torn is usually easy to helpwith physical therapy and/or a simple injection. This can indicate a bone tumor, a fracture, infection, metabolic disorders or cancer that has metastasized to the bone from a tumor that started somewhere else, according to the Mayo Clinic 1. The deposits may be asymptomatic or cause mechanical or inflammatory symptoms. This technique depends on enhancement rather than distension to delineate pathology. It is a fibrocartilaginous structure that deepens the shallow normally anteverted glenoid cavity. I call this the grey hair of the shoulder. Tendons turn grey on MRI when they age. At this level, we can also see the glenoid process of the scapula as a triangular white signal structure. Coronal oblique MRI shows bright fluid signal replacing the completely torn supraspinatus tendon (black arrow). WebThere were white spots like circles on my upper arm. WebWhite spots may be seen in several benign conditions such as migraine headache, however if in association with hypertension and diabetes, they may be representative of "mini strokes" which are often "silent" without symptoms. Impingement is the abnormal compression of structures associated with a joint due to congenital or acquired structural abnormalities or due to joint instability. The rotator interval narrows laterally and ends at the supraspinatus and subscapularis insertion. There were also images of my head and my neck of course which has been hurting for quite some time now. Richard Ramos answered. On average, theoutcomes forshoulder replacement patients are not nearly as good as hip or knee replacements (3). A few general comments about conventional and arthrographic MRI protocols will be made. Figure 2. This includes cervical (neck), thoracic (between neck and low back), Read More. A sublabral foramen is a complete detachment of the anterior superior labrum that reattaches anterior inferiorly. It internally rotates and adducts the arm. T2 hyperintensities (lesions). Neuroscience Group 1.47K subscribers 335 71K views 8 years ago Nurse Practitioner, Penny Bernards, discusses what white spots on your brain It is thought that the best way to assess the coracohumeral ligaments is by using an oblique sagittal image.