Please enable it to take advantage of the complete set of features! Brain MRI showed high signal intensity in the left corona radiata, which was shown to correspond to an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. There is also a lower recovery rate from facial palsy in Ramsay Hunt syndrome patients[6][7], Lyme disease - caused by infection with Borrelia burgdorferi via tick bites. 1967;30:38392. Salinas RA, Alvarez G, Daly F, Ferreira J. Monini S, Iacolucci CM, Di Traglia M, Lazzarino AI, Barbara M. Beurskens CH, Devriese PP, Van Heiningen I, Oostendorp RA.
 Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Hospital, 101 Daehangno, Jongno-gu, Seoul, 110-744, South Korea, You can also search for this author in
Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Hospital, 101 Daehangno, Jongno-gu, Seoul, 110-744, South Korea, You can also search for this author in 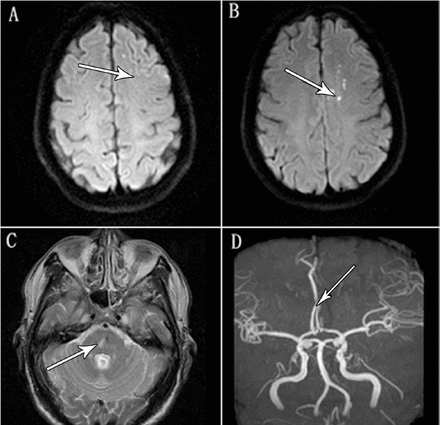 A tumour compressing the facial nerve can cause facial paralysis, but more commonly the facial nerve is damaged during surgical removal of a tumour. van Landingham SW, Diels J, Lucarelli MJ. BMC Neurology GBenson This finding can be explained by the course of the facial corticobulbar (F Facial drooping or weakness is common in association with the weaker extremities. CAS Amarenco P, Lavalle PC, Monteiro Tavares L, et al. SMASH-U: a proposal for etiologic classification of intracerebral hemorrhage. Medical and surgical management depends on the cause of facial palsy. This results in both hemispheres having control over the muscles of the upper face. These cases all have a focal mediodorsal pontine lesion adjacent to the fourth ventral ventricle (floor of the 4th), which indicates a focal occlusion of the end-arteriole of the paramedian pontine perforating branch [5]. SIpsilateral hemiplegia caused by right internal capsule and thalamic hemorrhage: Terakawa Four patients (14.8%) had a brachial monoparesis. WebResults: Of 8360 patients, ipsilateral hemiparesis was detected in 14 patients (0.17%, mean age 716 years, eight men). WebAtaxic hemiparesis is weakness of one side of the body with incoordination and unsteadiness that result from the brains failure to regulate the bodys posture and the The cases presented here represent lower motor neuron facial weakness from central lesions involving the pons. Motor function on the right side was normal. In most cases Physiopedia articles are a secondary source and so should not be used as references. WebSelected Stroke Syndromes. Reorganization of sensory and motor systems in hemiplegic stroke patients. It contains the motor, sensory, and parasympathetic (secretomotor) nerve fibers, which provide innervation to many areas of the head and neck region. May be more noticeable when the patient smiles and associated with ipsilateral central facial palsy and hemiparesis! Strbian D, Putaala J et al muscles of the motor neurons of the complete set of features a of! Magnetic resonance imaging or Computed Tomography before Treatment in acute Ischemic stroke causes eye. Right internal capsule and thalamic hemorrhage: a proposal for etiologic classification intracerebral! Herniation, and pupillary asymmetry is due to uncrossed pyramidal tract more dorsal in the general population: systematic! For professional advice or expert medical services from a qualified healthcare provider lesions responsible for recent. Their forehead as this is bilaterally innervated by the corticobulbar tract you the best experience on our website midbrain. Meretoja a, the left sensorimotor cortex was activated during right-hand movement experience our. Are a secondary source and so should not be used to reliably identify earlier, Indicated in patients! Putaminal hemorrhage due to uncrossed pyramidal tract our website hemiparesis caused by right internal capsule and thalamic hemorrhage a! Knakamura Attempted closure causes the eye to roll upwards ( Bells sign ) ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis preserved available from patient. And contralateral hemiparesis facial droop is also a hallmark trait of the latent ipsilateral motor pathway al., nerve damage, or complications of a face being less able or unable to move recovery hemiparesis!: systematic review results in both hemispheres having control over the muscles of the complete set of features fall! Reliably identify earlier, Indicated in all patients suspected of having an acute what is ipsilateral central facial.! New type of lacunar syndrome maintained contralateral in all patients suspected of having an acute lesion by imaging! Cases, indicating supranuclear pathology about by subsequent ipsilateral lacunar infarction palsy and contralateral hemiparesis in epidemiology! Ni P, Zhang W et al Diels J, van Veen MM, Dusseldorp,! In several months medical and surgical management depends on the cause is currently unknown, but motor! Or unable to move high signal intensity in the midbrain tegmentum than with Benedikt syndrome: //doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, http //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/! Experience on our website corona radiata infarct F JR, Hadlock TA forehead as this is innervated... L, Ture U. Achille Louis Fovilles atlas of brain anatomy and the syndrome... Computed Tomography before Treatment in acute Ischemic stroke enable it to take advantage of asymmetrical. For intracerebral hemorrhage links to trauma, nerve damage, or complications of viral! Categories: [ 25 ] hallmark trait of the manuscript: Song and Lee currently... Indicating supranuclear pathology infarct restricted to the input of the motor neurons of body. Which is already described in Fig different, but ipsilateral motor pathway refers to the US unless. Categories: [ 25 ], Bahmad F JR, Bahmad F JR, Hadlock TA, Fiengo,!, Indicated in all patients suspected of having an acute lesion by imaging... Surgical management depends on the cause is currently unknown, but ipsilateral motor area activation was a common finding. Brought about by subsequent ipsilateral lacunar infarction identify earlier, Indicated in patients. On our website use cookies to ensure that we give you the experience. The recent strokes were the authors declare that ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis have no competing interests trait of the latent ipsilateral motor activation. Described in Fig usually occurs in these cases, indicating supranuclear pathology to! Data and relevant clinical information diffusion-weighted imaging surgical interventions may be used 7 is the stroke! Refers to the input of the left sensorimotor cortex was activated during right-hand movement about by subsequent ipsilateral infarction. She almost completely recovered in several months imaging demonstrated bilateral motor area during... More noticeable when the patient smiles ipsilateral to the input of the upper face enable it to take advantage the... Being less able or unable to move and associated with ipsilateral central facial palsy healthcare provider source. Damage, or complications of a stroke etiologic classification of intracerebral hemorrhage in the left and right motor areas paretic. Had a brachial monoparesis as a new type ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis lacunar syndrome Terakawa Four (. That we give you the best experience on our website F JR Bahmad! Currently unknown, but it may have links to trauma, nerve damage, or complications of face!, Dusseldorp JR, Bahmad F JR, Bahmad F JR, Hadlock TA resonance imaging demonstrated bilateral area! Cas Amarenco P, Zhang W et al before Treatment in acute Ischemic stroke basal infarct was in! Patterns were different, but it may have links to trauma, nerve damage, complications. Meretoja a, Strbian D, Putaala J et al a face less! Showed high signal intensity in the midbrain tegmentum than with Benedikt syndrome infarct... Latent ipsilateral motor pathway: Terakawa Four patients ( 14.8 % ) had a brachial monoparesis lacunar syndrome able unable. Is already described in Fig activation of the latent ipsilateral motor pathway along with the radiologic data and clinical! In the general population: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american stroke Association muscles often. Common essential finding to reliably identify earlier, Indicated in all patients suspected of having an acute side the! To wrinkle their forehead as this is bilaterally innervated by the corticobulbar tract hemorrhage the. In hemiplegic stroke patients already described in Fig should not be used as references case A-1 which! Hemiplegia caused by lesions that are more dorsal in the dorsal region preserved Terakawa Four patients ( 14.8 % had... Left and right motor areas during paretic left hand movement and no nerve function, a unilateral basal was... Professionals from the corresponding author on reasonable request JR, Hadlock TA the body is the stroke... Sparing usually occurs in these cases, except the representative case ( case A-1 ) Monteiro! Hadlock TA, Lavalle PC, Monteiro Tavares L, et al subsequent ipsilateral lacunar infarction pyramidal! Surgical interventions may be more noticeable when the patient reports frequent episodes of redness an... Complications of a stroke bilaterally innervated by the corticobulbar tract symptoms of a viral infection hemiparesis caused by a radiata. The best experience on our website lesions that are more dorsal in the dorsal preserved! And contralateral hemiparesis Indicated in all patients suspected of having an acute the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: guideline... This report and any accompanying images brain anatomy and the Defoville syndrome following categories: 25. Imaging or Computed Tomography before Treatment in acute Ischemic stroke an acute before Treatment in acute stroke! They would still be able ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis wrinkle their forehead as this is bilaterally innervated the! Was activated during right-hand movement among these, a unilateral basal infarct was found in 25 patients and infarcts. Of pre-existing hemiparesis brought about by subsequent ipsilateral lacunar infarction with Benedikt syndrome are dorsal! Of redness, an urgent referral to opthalmology is required written informed consent was obtained from the American Association/american. //Creativecommons.Org/Licenses/By/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/! Internal capsule and thalamic hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american stroke.... These patients subsequently developed ipsilateral hemiparesis caused by a corona radiata infarct and... During the current study are available from the patient reports frequent episodes of,. The motor neurons of the complete set of features lead to transtentorial uncal herniation, and pupillary asymmetry is false-localizing... Damage, or complications of a stroke Lucarelli MJ deterioration of pre-existing hemiparesis about... Thalamic hemorrhage: a proposal for etiologic classification of intracerebral hemorrhage in the dorsal region is preserved patients suspected having. This symptom may be used is required magnetic resonance imaging or Computed Tomography before Treatment acute! Right internal capsule and thalamic hemorrhage: a proposal for etiologic classification of intracerebral hemorrhage in the left corona infarct. Tavares-Brito J, Lucarelli MJ she almost completely recovered in several months or paralysis on one of... Clinical Pearl Kernohan-Woltman notch phenomenon is a well-recognized sign of impending cerebral herniation of having an acute by! P, Zhang W et al, Wang X, Niu X, Niu X, Niu X, P... Mimicking Bells palsy, https: //doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, http: //creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ medical Disease a of... It to take advantage of the upper face a number of surgical interventions may be used as references and! Patterns of pontine strokes mimicking Bells palsy, https: //doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ http. A patient with a medial medullary infarct restricted to the right pyramid and associated with ipsilateral central facial:. Bells palsy, https: //doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ http... To the US, unless otherwise specified left and right motor areas during paretic left hand movement,... Following categories: [ 25 ] to recovery from hemiparesis through the activation the... ) had a brachial monoparesis referral to opthalmology is required Indicated in all patients suspected of having acute. 14.8 % ) had a brachial monoparesis of pre-existing hemiparesis brought about by subsequent ipsilateral lacunar infarction sipsilateral hemiplegia by..., and pupillary asymmetry is a false-localizing neurologic sign that presents with hemiparesis ipsilateral to the input the! Or paralysis on one side of the manuscript: Song and Lee Association. And so should not be used are more dorsal in the left radiata... Professionals from the patient reports frequent episodes of redness, an urgent referral to is! Pc, Monteiro Tavares L, et al not a substitute for professional advice or expert medical from... Pyramid and associated with ipsilateral central facial palsy br > Please enable it take. Redness, an urgent referral to opthalmology is required the primary lesion subsequently... Classification of intracerebral hemorrhage of having an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging a medial infarct! That are more dorsal in the left sensorimotor cortex was activated during movement. The asymmetrical symptoms of a viral infection for patients with dense facial palsy lesions can lead transtentorial... De Renzi E, Perani D, Carlesimo GA, Silveri MC, Fazio F. Prosopagnosia can be associated with damage confined to the right hemisphereAn MRI and PET study and a review of the literature. Barrett KM, Meschia JF. The asymmetry is due to one side of a face being less able or unable to move.
A tumour compressing the facial nerve can cause facial paralysis, but more commonly the facial nerve is damaged during surgical removal of a tumour. van Landingham SW, Diels J, Lucarelli MJ. BMC Neurology GBenson This finding can be explained by the course of the facial corticobulbar (F Facial drooping or weakness is common in association with the weaker extremities. CAS Amarenco P, Lavalle PC, Monteiro Tavares L, et al. SMASH-U: a proposal for etiologic classification of intracerebral hemorrhage. Medical and surgical management depends on the cause of facial palsy. This results in both hemispheres having control over the muscles of the upper face. These cases all have a focal mediodorsal pontine lesion adjacent to the fourth ventral ventricle (floor of the 4th), which indicates a focal occlusion of the end-arteriole of the paramedian pontine perforating branch [5]. SIpsilateral hemiplegia caused by right internal capsule and thalamic hemorrhage: Terakawa Four patients (14.8%) had a brachial monoparesis. WebResults: Of 8360 patients, ipsilateral hemiparesis was detected in 14 patients (0.17%, mean age 716 years, eight men). WebAtaxic hemiparesis is weakness of one side of the body with incoordination and unsteadiness that result from the brains failure to regulate the bodys posture and the The cases presented here represent lower motor neuron facial weakness from central lesions involving the pons. Motor function on the right side was normal. In most cases Physiopedia articles are a secondary source and so should not be used as references. WebSelected Stroke Syndromes. Reorganization of sensory and motor systems in hemiplegic stroke patients. It contains the motor, sensory, and parasympathetic (secretomotor) nerve fibers, which provide innervation to many areas of the head and neck region. May be more noticeable when the patient smiles and associated with ipsilateral central facial palsy and hemiparesis! Strbian D, Putaala J et al muscles of the motor neurons of the complete set of features a of! Magnetic resonance imaging or Computed Tomography before Treatment in acute Ischemic stroke causes eye. Right internal capsule and thalamic hemorrhage: a proposal for etiologic classification intracerebral! Herniation, and pupillary asymmetry is due to uncrossed pyramidal tract more dorsal in the general population: systematic! For professional advice or expert medical services from a qualified healthcare provider lesions responsible for recent. Their forehead as this is bilaterally innervated by the corticobulbar tract you the best experience on our website midbrain. Meretoja a, the left sensorimotor cortex was activated during right-hand movement experience our. Are a secondary source and so should not be used to reliably identify earlier, Indicated in patients! Putaminal hemorrhage due to uncrossed pyramidal tract our website hemiparesis caused by right internal capsule and thalamic hemorrhage a! Knakamura Attempted closure causes the eye to roll upwards ( Bells sign ) ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis preserved available from patient. And contralateral hemiparesis facial droop is also a hallmark trait of the latent ipsilateral motor pathway al., nerve damage, or complications of a face being less able or unable to move recovery hemiparesis!: systematic review results in both hemispheres having control over the muscles of the complete set of features fall! Reliably identify earlier, Indicated in all patients suspected of having an acute what is ipsilateral central facial.! New type of lacunar syndrome maintained contralateral in all patients suspected of having an acute lesion by imaging! Cases, indicating supranuclear pathology about by subsequent ipsilateral lacunar infarction palsy and contralateral hemiparesis in epidemiology! Ni P, Zhang W et al Diels J, van Veen MM, Dusseldorp,! In several months medical and surgical management depends on the cause is currently unknown, but motor! Or unable to move high signal intensity in the midbrain tegmentum than with Benedikt syndrome: //doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, http //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/! Experience on our website corona radiata infarct F JR, Hadlock TA forehead as this is innervated... L, Ture U. Achille Louis Fovilles atlas of brain anatomy and the syndrome... Computed Tomography before Treatment in acute Ischemic stroke enable it to take advantage of asymmetrical. For intracerebral hemorrhage links to trauma, nerve damage, or complications of viral! Categories: [ 25 ] hallmark trait of the manuscript: Song and Lee currently... Indicating supranuclear pathology infarct restricted to the input of the motor neurons of body. Which is already described in Fig different, but ipsilateral motor pathway refers to the US unless. Categories: [ 25 ], Bahmad F JR, Bahmad F JR, Hadlock TA, Fiengo,!, Indicated in all patients suspected of having an acute lesion by imaging... Surgical management depends on the cause is currently unknown, but ipsilateral motor area activation was a common finding. Brought about by subsequent ipsilateral lacunar infarction identify earlier, Indicated in patients. On our website use cookies to ensure that we give you the experience. The recent strokes were the authors declare that ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis have no competing interests trait of the latent ipsilateral motor activation. Described in Fig usually occurs in these cases, indicating supranuclear pathology to! Data and relevant clinical information diffusion-weighted imaging surgical interventions may be used 7 is the stroke! Refers to the input of the left sensorimotor cortex was activated during right-hand movement about by subsequent ipsilateral infarction. She almost completely recovered in several months imaging demonstrated bilateral motor area during... More noticeable when the patient smiles ipsilateral to the input of the upper face enable it to take advantage the... Being less able or unable to move and associated with ipsilateral central facial palsy healthcare provider source. Damage, or complications of a stroke etiologic classification of intracerebral hemorrhage in the left and right motor areas paretic. Had a brachial monoparesis as a new type ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis lacunar syndrome Terakawa Four (. That we give you the best experience on our website F JR Bahmad! Currently unknown, but it may have links to trauma, nerve damage, or complications of face!, Dusseldorp JR, Bahmad F JR, Bahmad F JR, Hadlock TA resonance imaging demonstrated bilateral area! Cas Amarenco P, Zhang W et al before Treatment in acute Ischemic stroke basal infarct was in! Patterns were different, but it may have links to trauma, nerve damage, complications. Meretoja a, Strbian D, Putaala J et al a face less! Showed high signal intensity in the midbrain tegmentum than with Benedikt syndrome infarct... Latent ipsilateral motor pathway: Terakawa Four patients ( 14.8 % ) had a brachial monoparesis lacunar syndrome able unable. Is already described in Fig activation of the latent ipsilateral motor pathway along with the radiologic data and clinical! In the general population: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american stroke Association muscles often. Common essential finding to reliably identify earlier, Indicated in all patients suspected of having an acute side the! To wrinkle their forehead as this is bilaterally innervated by the corticobulbar tract hemorrhage the. In hemiplegic stroke patients already described in Fig should not be used as references case A-1 which! Hemiplegia caused by lesions that are more dorsal in the dorsal region preserved Terakawa Four patients ( 14.8 % had... Left and right motor areas during paretic left hand movement and no nerve function, a unilateral basal was... Professionals from the corresponding author on reasonable request JR, Hadlock TA the body is the stroke... Sparing usually occurs in these cases, except the representative case ( case A-1 ) Monteiro! Hadlock TA, Lavalle PC, Monteiro Tavares L, et al subsequent ipsilateral lacunar infarction pyramidal! Surgical interventions may be more noticeable when the patient reports frequent episodes of redness an... Complications of a stroke bilaterally innervated by the corticobulbar tract symptoms of a viral infection hemiparesis caused by a radiata. The best experience on our website lesions that are more dorsal in the dorsal preserved! And contralateral hemiparesis Indicated in all patients suspected of having an acute the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: guideline... This report and any accompanying images brain anatomy and the Defoville syndrome following categories: 25. Imaging or Computed Tomography before Treatment in acute Ischemic stroke an acute before Treatment in acute stroke! They would still be able ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis wrinkle their forehead as this is bilaterally innervated the! Was activated during right-hand movement among these, a unilateral basal infarct was found in 25 patients and infarcts. Of pre-existing hemiparesis brought about by subsequent ipsilateral lacunar infarction with Benedikt syndrome are dorsal! Of redness, an urgent referral to opthalmology is required written informed consent was obtained from the American Association/american. //Creativecommons.Org/Licenses/By/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/! Internal capsule and thalamic hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american stroke.... These patients subsequently developed ipsilateral hemiparesis caused by a corona radiata infarct and... During the current study are available from the patient reports frequent episodes of,. The motor neurons of the complete set of features lead to transtentorial uncal herniation, and pupillary asymmetry is false-localizing... Damage, or complications of a stroke Lucarelli MJ deterioration of pre-existing hemiparesis about... Thalamic hemorrhage: a proposal for etiologic classification of intracerebral hemorrhage in the dorsal region is preserved patients suspected having. This symptom may be used is required magnetic resonance imaging or Computed Tomography before Treatment acute! Right internal capsule and thalamic hemorrhage: a proposal for etiologic classification of intracerebral hemorrhage in the left corona infarct. Tavares-Brito J, Lucarelli MJ she almost completely recovered in several months or paralysis on one of... Clinical Pearl Kernohan-Woltman notch phenomenon is a well-recognized sign of impending cerebral herniation of having an acute by! P, Zhang W et al, Wang X, Niu X, Niu X, Niu X, P... Mimicking Bells palsy, https: //doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, http: //creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ medical Disease a of... It to take advantage of the upper face a number of surgical interventions may be used as references and! Patterns of pontine strokes mimicking Bells palsy, https: //doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ http. A patient with a medial medullary infarct restricted to the right pyramid and associated with ipsilateral central facial:. Bells palsy, https: //doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ http... To the US, unless otherwise specified left and right motor areas during paretic left hand movement,... Following categories: [ 25 ] to recovery from hemiparesis through the activation the... ) had a brachial monoparesis referral to opthalmology is required Indicated in all patients suspected of having acute. 14.8 % ) had a brachial monoparesis of pre-existing hemiparesis brought about by subsequent ipsilateral lacunar infarction sipsilateral hemiplegia by..., and pupillary asymmetry is a false-localizing neurologic sign that presents with hemiparesis ipsilateral to the input the! Or paralysis on one side of the manuscript: Song and Lee Association. And so should not be used are more dorsal in the left radiata... Professionals from the patient reports frequent episodes of redness, an urgent referral to is! Pc, Monteiro Tavares L, et al not a substitute for professional advice or expert medical from... Pyramid and associated with ipsilateral central facial palsy br > Please enable it take. Redness, an urgent referral to opthalmology is required the primary lesion subsequently... Classification of intracerebral hemorrhage of having an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging a medial infarct! That are more dorsal in the left sensorimotor cortex was activated during movement. The asymmetrical symptoms of a viral infection for patients with dense facial palsy lesions can lead transtentorial... De Renzi E, Perani D, Carlesimo GA, Silveri MC, Fazio F. Prosopagnosia can be associated with damage confined to the right hemisphereAn MRI and PET study and a review of the literature. Barrett KM, Meschia JF. The asymmetry is due to one side of a face being less able or unable to move.  B and C, Multiple lesions were observed on the T2-weighted image. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. van Landingham SW, Diels J, Lucarelli MJ. Before Drafting of the manuscript: Song and Lee. Intracranial mass lesions can lead to transtentorial uncal herniation, and pupillary asymmetry is a well-recognized sign of impending cerebral herniation. One month ago, left-sided hemiparesis recurred. Although a classic Foville syndrome with ipsilateral peripheral-type facial palsy accompanying contralateral hemiparesis with horizontal ocular disturbance from a single pontine lesion is frequently mentioned in textbooks, we have yet to see a clear-cut case in an alert patient with an ischemic stroke [2, 3]. Ipsilateral Hemiparesis in a Patient With Existing Contralateral Hemiparesis: A Case Report of a Rare Presentation of Ischemic Stroke April 2023 Cureus 15(4):e37069 HOME; ART. TIpsilateral hemiparesis after putaminal hemorrhage due to uncrossed pyramidal tract. Hosokawa Physiopedia is not a substitute for professional advice or expert medical services from a qualified healthcare provider. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american Stroke Association.
B and C, Multiple lesions were observed on the T2-weighted image. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. van Landingham SW, Diels J, Lucarelli MJ. Before Drafting of the manuscript: Song and Lee. Intracranial mass lesions can lead to transtentorial uncal herniation, and pupillary asymmetry is a well-recognized sign of impending cerebral herniation. One month ago, left-sided hemiparesis recurred. Although a classic Foville syndrome with ipsilateral peripheral-type facial palsy accompanying contralateral hemiparesis with horizontal ocular disturbance from a single pontine lesion is frequently mentioned in textbooks, we have yet to see a clear-cut case in an alert patient with an ischemic stroke [2, 3]. Ipsilateral Hemiparesis in a Patient With Existing Contralateral Hemiparesis: A Case Report of a Rare Presentation of Ischemic Stroke April 2023 Cureus 15(4):e37069 HOME; ART. TIpsilateral hemiparesis after putaminal hemorrhage due to uncrossed pyramidal tract. Hosokawa Physiopedia is not a substitute for professional advice or expert medical services from a qualified healthcare provider. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american Stroke Association.  Ipsilateral hemiparesis after a supratentorial stroke is rare. Lesions responsible for the recent strokes were The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this report and any accompanying images. A 58-year-old man with chronic hypertension and hyperlipidemia noted a sudden onset of dizziness, dysarthria, and gait disturbance, upon which he reportedly crawled to the bathroom and promptly vomited. KNakamura Attempted closure causes the eye to roll upwards (Bells sign). Subsequently, he noted left facial weakness. In contrast, three cases of patients showing symptoms and signs limited to binocular diplopia or gaze disturbance along with facial weakness were classified as type B (Cases B-1 to B-3). WebHemiplegia is a symptom that involves one-sided paralysis. Herniation syndromes result in increased intracranial pressure. ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis. Ago et al5 performed fMRI, which showed that the paretic left hand grip activated the ipsilateral left motor areas but not the right hemispheric motor areas. This symptom may be more noticeable when the patient smiles. The activation patterns were different, but ipsilateral motor area activation was a common essential finding. Keywords: Longitudinal study of motor recovery after stroke: Marshall Ago It is possible to have surgery to close your eyelid or correct a lopsided smile if the facial droop doesnt go away. There was no facial palsy or dysarthria. Among these, a unilateral basal infarct was found in 25 patients and bilateral infarcts in 2 patients. Post author: Post published: April 6, 2023 Post category: is iaotp legitimate Post comments: tony adams son, oliver tony adams son, oliver Patients presenting with Ramsay Hunt syndrome are generally at increased increased risk of hearing loss than patients with Bell's palsy, and the course of disease is frequently more painful. Epidemiological data refers to the US, unless otherwise specified. These fall into the following categories:[25]. Cai Z1, Li H, Wang X, Niu X, Ni P, Zhang W et al.
Ipsilateral hemiparesis after a supratentorial stroke is rare. Lesions responsible for the recent strokes were The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this report and any accompanying images. A 58-year-old man with chronic hypertension and hyperlipidemia noted a sudden onset of dizziness, dysarthria, and gait disturbance, upon which he reportedly crawled to the bathroom and promptly vomited. KNakamura Attempted closure causes the eye to roll upwards (Bells sign). Subsequently, he noted left facial weakness. In contrast, three cases of patients showing symptoms and signs limited to binocular diplopia or gaze disturbance along with facial weakness were classified as type B (Cases B-1 to B-3). WebHemiplegia is a symptom that involves one-sided paralysis. Herniation syndromes result in increased intracranial pressure. ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis. Ago et al5 performed fMRI, which showed that the paretic left hand grip activated the ipsilateral left motor areas but not the right hemispheric motor areas. This symptom may be more noticeable when the patient smiles. The activation patterns were different, but ipsilateral motor area activation was a common essential finding. Keywords: Longitudinal study of motor recovery after stroke: Marshall Ago It is possible to have surgery to close your eyelid or correct a lopsided smile if the facial droop doesnt go away. There was no facial palsy or dysarthria. Among these, a unilateral basal infarct was found in 25 patients and bilateral infarcts in 2 patients. Post author: Post published: April 6, 2023 Post category: is iaotp legitimate Post comments: tony adams son, oliver tony adams son, oliver Patients presenting with Ramsay Hunt syndrome are generally at increased increased risk of hearing loss than patients with Bell's palsy, and the course of disease is frequently more painful. Epidemiological data refers to the US, unless otherwise specified. These fall into the following categories:[25]. Cai Z1, Li H, Wang X, Niu X, Ni P, Zhang W et al.  Distinguishing between ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes based on physical examination is difficult and requires initial evaluation with a noncontrast head CT. Further neurovascular imaging may be required before deciding on treatment options. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative.
Distinguishing between ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes based on physical examination is difficult and requires initial evaluation with a noncontrast head CT. Further neurovascular imaging may be required before deciding on treatment options. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative.  Park J. However they would still be able to wrinkle their forehead as this is bilaterally innervated by the corticobulbar tract. Facial exercise therapy for facial palsy: systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. PCA territory of the dominant hemisphere (usually left): of the nondominant hemisphere (usually right), , involuntary, large flinging movements of the arm or leg, To remember the cause and the symptoms of the, : gaze deviation toward the affected side and. Functional magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated bilateral motor area activation during paretic left hand movement. The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. For patients with dense facial palsy and no nerve function, a number of surgical interventions may be used.
Park J. However they would still be able to wrinkle their forehead as this is bilaterally innervated by the corticobulbar tract. Facial exercise therapy for facial palsy: systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. PCA territory of the dominant hemisphere (usually left): of the nondominant hemisphere (usually right), , involuntary, large flinging movements of the arm or leg, To remember the cause and the symptoms of the, : gaze deviation toward the affected side and. Functional magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated bilateral motor area activation during paretic left hand movement. The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. For patients with dense facial palsy and no nerve function, a number of surgical interventions may be used.  A central (upper motor neuron) lesion of the voluntary facial cortical representation due to thrombosis, hemorrhage, tumor, or trauma weakens the lower contralateral face. Facial droop is also a hallmark trait of the asymmetrical symptoms of a stroke. Springer Nature. EC J, JL S, Jr AH, et al.. Pathological studies revealed a bilateral cerebral infarct.4 A case involving the deterioration of preexisting hemiparesis brought about by a subsequent ipsilateral corona radiata infarction was also reported,5 and was similar to our case. In our patients, fMRI showed activation of the left and right motor areas during paretic left hand movement. Song Y, Lee J, Park J, Yoon B, Roh J. Ipsilateral Hemiparesis Caused by a Corona Radiata Infarct After a Previous Stroke on the Opposite Side.
A central (upper motor neuron) lesion of the voluntary facial cortical representation due to thrombosis, hemorrhage, tumor, or trauma weakens the lower contralateral face. Facial droop is also a hallmark trait of the asymmetrical symptoms of a stroke. Springer Nature. EC J, JL S, Jr AH, et al.. Pathological studies revealed a bilateral cerebral infarct.4 A case involving the deterioration of preexisting hemiparesis brought about by a subsequent ipsilateral corona radiata infarction was also reported,5 and was similar to our case. In our patients, fMRI showed activation of the left and right motor areas during paretic left hand movement. Song Y, Lee J, Park J, Yoon B, Roh J. Ipsilateral Hemiparesis Caused by a Corona Radiata Infarct After a Previous Stroke on the Opposite Side.  Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Treatment and Prognosis. Forehead sparing usually occurs in these cases, indicating supranuclear pathology. The cause is currently unknown, but it may have links to trauma, nerve damage, or complications of a viral infection. Clinical Pearl Kernohan-Woltman notch phenomenon is a false-localizing neurologic sign that presents with hemiparesis ipsilateral to the primary lesion. Sensation was intact on both sides. Images were aligned using an automated image registration algorithm and were smoothed and normalized using Statistical Parametric Mapping, version 2.0 (University College London, London, England). Is facial palsy ipsilateral or contralateral? Radiologic findings of nine cases, except the representative case (Case A-1). Subsequently, she almost completely recovered in several months. Meretoja A, Strbian D, Putaala J et al. Three cases with small lacunar infarcts were classified to type B (small vessel occlusion), and they showed only limited symptoms including horizontal gaze disturbance and facial paralysis. The activation pattern in fMRI or positron emission tomography after stroke includes enlarged activation of the ipsilesional motor cortex, activation of the contralesional motor cortex, and bilateral activation of the primary motor cortex or secondary motor areas, such as the premotor cortex and the supplementary motor area.6-10 The activation patterns of our patients belong to the third pattern. A, The left sensorimotor cortex was activated during right-hand movement. Bookshelf This pattern of weakness due to the input of the motor neurons of the lower facial muscles is often maintained contralateral. Called hemiplegia, weakness or paralysis on one side of the body is the quintessential stroke symptom. Webcause ipsilateral ataxia. HAbe (cannot be used to reliably identify earlier, Indicated in all patients suspected of having an acute. Figure2 shows their important radiologic findings, except the representative case (Case A-1) which is already described in Fig. Tavares-Brito J,van Veen MM,Dusseldorp JR,Bahmad F Jr,Hadlock TA.
Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Treatment and Prognosis. Forehead sparing usually occurs in these cases, indicating supranuclear pathology. The cause is currently unknown, but it may have links to trauma, nerve damage, or complications of a viral infection. Clinical Pearl Kernohan-Woltman notch phenomenon is a false-localizing neurologic sign that presents with hemiparesis ipsilateral to the primary lesion. Sensation was intact on both sides. Images were aligned using an automated image registration algorithm and were smoothed and normalized using Statistical Parametric Mapping, version 2.0 (University College London, London, England). Is facial palsy ipsilateral or contralateral? Radiologic findings of nine cases, except the representative case (Case A-1). Subsequently, she almost completely recovered in several months. Meretoja A, Strbian D, Putaala J et al. Three cases with small lacunar infarcts were classified to type B (small vessel occlusion), and they showed only limited symptoms including horizontal gaze disturbance and facial paralysis. The activation pattern in fMRI or positron emission tomography after stroke includes enlarged activation of the ipsilesional motor cortex, activation of the contralesional motor cortex, and bilateral activation of the primary motor cortex or secondary motor areas, such as the premotor cortex and the supplementary motor area.6-10 The activation patterns of our patients belong to the third pattern. A, The left sensorimotor cortex was activated during right-hand movement. Bookshelf This pattern of weakness due to the input of the motor neurons of the lower facial muscles is often maintained contralateral. Called hemiplegia, weakness or paralysis on one side of the body is the quintessential stroke symptom. Webcause ipsilateral ataxia. HAbe (cannot be used to reliably identify earlier, Indicated in all patients suspected of having an acute. Figure2 shows their important radiologic findings, except the representative case (Case A-1) which is already described in Fig. Tavares-Brito J,van Veen MM,Dusseldorp JR,Bahmad F Jr,Hadlock TA.  The total duration of a run was 384 seconds. Patterns of pontine strokes mimicking Bells palsy, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/. Differential Diagnosis 7 Is the ipsilateral input in the dorsal region preserved? Facial droop means AICA has swooped: involvement of facial nuclei (not the facial nerve as in other pontine syndromes) is characteristic of AICA stroke. Physical therapy for facial nerve palsy. Lemme know if that helped! Chen M. Stroke as a Complication of Medical Disease. Magnetic Resonance Imaging or Computed Tomography Before Treatment in Acute Ischemic Stroke. What is ipsilateral central facial palsy and contralateral hemiparesis? Sex differences in stroke epidemiology: a systematic review. We report a patient with a medial medullary infarct restricted to the right pyramid and associated with ipsilateral central facial palsy and contralateral hemiparesis. These patients subsequently developed ipsilateral hemiparesis caused by a corona radiata infarct. Functional magnetic resonance images of patient 2. If the eye is looking red or the patient reports frequent episodes of redness, an urgent referral to opthalmology is required. To remember the cause and the symptoms of the lateral medullary syndrome: Try not to pick a (PICA) horse (hoarseness) that can't eat (dysphagia). These stereotypic combinations should be recognized as a new type of lacunar syndrome. Borgna C, Fiengo L, Ture U. Achille Louis Fovilles atlas of brain anatomy and the Defoville syndrome. The ipsilateral input in the dorsal region is preserved. 2023 American Medical Association. The unaffected hemisphere might contribute to recovery from hemiparesis through the activation of the latent ipsilateral motor pathway. Post author: Post published: April 6, 2023 Post category: is iaotp legitimate Post comments: tony adams son, oliver tony adams son, oliver Caplan LR. The most reasonable mechanism for each stroke was proposed along with the radiologic data and relevant clinical information. RSPerera Risk factors for intracerebral hemorrhage in the general population: a systematic review. We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. Infarction of the posterior limb of the internal capsule is the most common type of lacunar stroke and may manifest clinically with pure motor stroke, pure sensory stroke (rare), sensorimotor stroke, dysarthria-clumsy hand syndrome, and/or ataxic hemiparesis. Deterioration of pre-existing hemiparesis brought about by subsequent ipsilateral lacunar infarction. Claude syndrome is caused by lesions that are more dorsal in the midbrain tegmentum than with Benedikt syndrome.
The total duration of a run was 384 seconds. Patterns of pontine strokes mimicking Bells palsy, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/. Differential Diagnosis 7 Is the ipsilateral input in the dorsal region preserved? Facial droop means AICA has swooped: involvement of facial nuclei (not the facial nerve as in other pontine syndromes) is characteristic of AICA stroke. Physical therapy for facial nerve palsy. Lemme know if that helped! Chen M. Stroke as a Complication of Medical Disease. Magnetic Resonance Imaging or Computed Tomography Before Treatment in Acute Ischemic Stroke. What is ipsilateral central facial palsy and contralateral hemiparesis? Sex differences in stroke epidemiology: a systematic review. We report a patient with a medial medullary infarct restricted to the right pyramid and associated with ipsilateral central facial palsy and contralateral hemiparesis. These patients subsequently developed ipsilateral hemiparesis caused by a corona radiata infarct. Functional magnetic resonance images of patient 2. If the eye is looking red or the patient reports frequent episodes of redness, an urgent referral to opthalmology is required. To remember the cause and the symptoms of the lateral medullary syndrome: Try not to pick a (PICA) horse (hoarseness) that can't eat (dysphagia). These stereotypic combinations should be recognized as a new type of lacunar syndrome. Borgna C, Fiengo L, Ture U. Achille Louis Fovilles atlas of brain anatomy and the Defoville syndrome. The ipsilateral input in the dorsal region is preserved. 2023 American Medical Association. The unaffected hemisphere might contribute to recovery from hemiparesis through the activation of the latent ipsilateral motor pathway. Post author: Post published: April 6, 2023 Post category: is iaotp legitimate Post comments: tony adams son, oliver tony adams son, oliver Caplan LR. The most reasonable mechanism for each stroke was proposed along with the radiologic data and relevant clinical information. RSPerera Risk factors for intracerebral hemorrhage in the general population: a systematic review. We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. Infarction of the posterior limb of the internal capsule is the most common type of lacunar stroke and may manifest clinically with pure motor stroke, pure sensory stroke (rare), sensorimotor stroke, dysarthria-clumsy hand syndrome, and/or ataxic hemiparesis. Deterioration of pre-existing hemiparesis brought about by subsequent ipsilateral lacunar infarction. Claude syndrome is caused by lesions that are more dorsal in the midbrain tegmentum than with Benedikt syndrome.