short run supply curve formula
You can easily remember all of the shocks that shift SRAS by thinking of. Because the market price is not affected by the output choice of a single firm, the marginal revenue the firm gains by producing one more unit is always the market price. Consider the case of a single radish producer, Tony Gortari. Total economic losses at an output of 4,444 pounds per month are thus $222.20 per month (=4,444$0.05). Events like these are called shocks because they arent anticipated.
The break-even price is when the market price is equal to the minimum average total cost of production. Why does expecting higher inflation lower supply? Look carefully at the rectangle that shows economic profit in Panel (b) of Figure 9.7 Applying the Marginal Decision Rule. Here, the firm's shortrun supply curve is the portion of the marginal cost curve labeled ef. The crucial test of whether to operate or shut down lies in the relationship between price and average variable cost. Whenever price falls below average variable cost, the firm will shut down, reducing its production to zero. Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices. If factors of production get cheaper, or producers think they will get cheaper, then SRAS increases. It is shown graphically by the area of the shaded rectangle in Panel (b); this area equals the vertical distance between marginal revenue (MR) and average total cost (ATC) at an output of 6,700 pounds of radishes times the number of pounds of radishes produced, 6,700, in Figure 9.7 Applying the Marginal Decision Rule. If the market price of a pound of radishes is $0.40, then the marginal revenue is $0.40. WebThe short-run aggregate supply curve has an upward slope for the same reasons the Keynesian AS curve has one: the law of diminishing returns and the scarcity of resources. If a firm gets a higher price, they will make a higher profit by selling more, so quantity supplied increases when price increases. At any price, the greater the quantity a perfectly competitive firm sells, the greater its total revenue. Panel (a) shows the market for radishes; the market demand curve (D), and supply curve (S) that we had in Figure 9.3 The Market for Radishes; the market price is $0.40 per pound. We will use this cell as the correct optimal solution in all cases, including the shutdown case. topics include sticky wage theory and menu cost theory, as well as the causes of short-run aggregate supply shocks. It is usually an upward-sloping curve as the relationship between price increases is directly proportional to the rise in output levels. After all, wages are usually set for long time periods because of labor contracts. The marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line at the market price, and average revenue equals the market price. Higher inflation will likely pave the way to an expansionary event within the economy. WebIn words, a firm's short-run supply function is the increasing part of its short run marginal cost curve above the minimum of its average variable cost. A firm that is experiencing economic losseswhose economic profits have become negativein the short run may either continue to produce or shut down its operations, reducing its output to zero. The relationship between market price and the firms total revenue curve is a crucial one. Prepare to Eat Your Hat, USA Today, April 9, 2003: p. 3B. The case where the firm is incurring shortrun losses but continues to operate is illustrated graphically in Figure (a). Why did Colussy buy Iridium? On the other hand, when the price level decreases, producers are willing to make less because sticky wages make workers not as good of a deal and producers sell less. WebShort-run and long-run are the two final domestic supply types. When the marginal value is less than the average value, the average value will be falling. Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit shows the total cost curve for Mr. Gortari, as well as the total revenue curve for a price of $0.40 per pound. At this point, economic profit equals zero. At a price of $81, Acmes marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line at $81. Direct link to Xin Hwei Lim's post Should the Phillips Curve, Posted 4 years ago. But it was in the aftermath of 9/11 that its subscriber list really began to grow and its re-opening was deemed a stroke of genius. There is no reason for the profit-maximizing quantity to correspond to the lowest point on the ATC curve; it does not in this case. I assume the expectation of higher inflation would lower the supply temporarily, as businesses and firms are WAITING until the economy begins to heal before they begin operating as usual, yet while reducing their current output to save money, [Click here to compare your answer to the correct answer]. Mr. Gortari achieves the greatest profit possible by producing 6,700 pounds of radishes per month, the quantity at which the total cost and total revenue curves have the same slope. In the market model, supply slopes up because of the profit motive of individual firms. Mr. Gortari faces a demand curve that is a horizontal line at the market price. We can think of it as the increase in total revenue associated with a 1-unit increase in output. Should the Phillips Curve be depicted as straight or concave? We assume he can sell all the radishes he wants at the market price; there would be no reason to charge a lower price. Direct link to Del Cueto Ashley's post Assume that crayons can b, Posted 3 years ago. It is an indicator of the adjustments the economy makes in the event of changes. The SRAS curve slopes up for two reasons: sticky input prices (like wages) and sticky output prices (also called menu costs). 2023 Course Hero, Inc. All rights reserved. Because revenues are rising faster than costs, profits rise with increased output. One of the exercise questions says that due to expected lower inflation, the SRS shifts to the right. We saw an example of a horizontal demand curve in the chapter on elasticity. [14] So maybe you dont raise your prices. Looking at Figure 9.10 Marginal Cost and Supply, we see that profit-maximizing choices by firms in a perfectly competitive market will generate a market supply curve that reflects marginal cost. The equation for the upward sloping aggregate supply curve, in the short run, is Y = Ynatural + a (P - Pexpected). Shortrun supply curve. The short run supply function of a firm with "typical" cost curves is shown in the figure. We will use this cell as the correct optimal solution in all cases, including the shutdown case. WebShort-run and long-run are the two final domestic supply types. WebTranscribed Image Text: Suppose the economy's short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve is given by the following equation: Quantity of Output Supplied = The Greek letter a represents a number that determines how much output responds to unexpected changes in the price level. The firms supply curve in the short run is its marginal cost curve for prices above the average variable cost. The SRAS curve shows that as the price level increases and you move along the SRAS, the amount of real GDP that will be produced in an economy increases. Lets start with the first reason producers might continue despite inflation: sticky input prices. Wait a minute, does that mean that firms respond to inflation by producing. Economists used to believe that all prices were flexible. First, determine the enterprises profit-maximising output degree when the market cost price is As Mr. Gortari expands output above 1,500 pounds per month, total revenue becomes greater than total cost. For perfectly competitive firms, the price is very much like the weather: they may complain about it, but in perfect competition there is nothing any of them can do about it. Finding the output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost is thus an application of our marginal decision rule. It is easy to see that Solver has been run because at q 10 in cell B8, M R = M C since P = 4 and cell B18 reports M C = 4. When marginal revenue is below marginal cost, the firm is losing money, and consequently, it must reduce its output. In selecting the quantity of that output, one important consideration is the revenue the firm will gain by producing it. Marginal revenue equals the market price. The economy is always operating somewhere on the short-run Phillips curve (SRPC) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment. Economists had to rethink what they thought they knew about how well prices adjust. Interestingly, this happens if firms expect that this will happen too. Fig.
On the other hand, anything that makes production cheaper or easier to produce will cause the SRAS curve to shift to the right. In the equation, Y is the production of the economy, Y* is the natural level of production, coefficient is always positive, P is the price level, and In general, the firm makes positive profits whenever its average total cost curve lies below its marginal revenue curve. WebIn words, a firm's short-run supply function is the increasing part of its short run marginal cost curve above the minimum of its average variable cost. WebFig. The area of this rectangle is easily calculated. The firm is better off continuing its operations because it can cover its variable costs and use any remaining revenues to pay off some of its fixed costs. Hence, the firm's fixed costs are considered sunk costs and will not have any bearing on whether the firm decides to shut down. The average and marginal revenue curves are given by the same horizontal line. 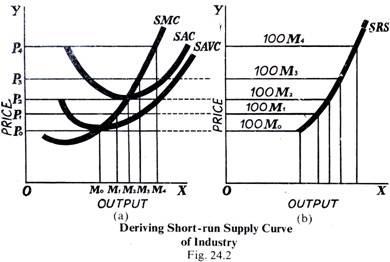 In this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms and graphs related to short-run aggregate supply. It is easy to see that Solver has been run because at q 10 in cell B8, M R = M C since P = 4 and cell B18 reports M C = 4. Now suppose that the astrological forecast industry consists of Madame LaFarge and thousands of other firms similar to hers. WebThe economy is always operating somewhere on the short-run Phillips curve (SRPC) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment. STEP Click on C8 to reveal its formula: = IF (max profit >= d, q, 0). The slope of a total revenue curve is particularly important. Direct link to melanie's post It doesn't matter as long, Posted 3 years ago. The firms supply curve in the short run is its marginal cost curve for prices greater than the minimum average variable cost. Why would producers see inflation and think, lets all make more stuff? Notice that the greater the price, the steeper the total revenue curve is. Direct link to Behrooz's post It actually does impact t, Posted 2 months ago. In the wake of September 11, 2001, and then the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq, demand for secure communications in remote locations skyrocketed. #1 Aggregate Supply in Short Run. In this case, assume that a = : $2 billion. The fact that the firm can pay its variable costs is all that matters because in the shortrun, the firm's fixed costs are sunk; the firm must pay its fixed costs regardless of whether or not it decides to shut down. Now, using the marginal cost and average total cost curves for Acme shown here: Estimate Acmes profit-maximizing output per day (assume the firm selects a whole number). Its fixed in place and, if its moving, its doing so really slowly! Tony Gortari experiences a loss when price drops below ATC, as it does in Panel (b) as a result of a reduction in demand. That is, when the actual price level exceeds the It is because, in the short run, fixed cost is paid regardless of the amount produced. bookmarked pages associated with this title. It rises at an increasing rate over the range of diminishing marginal returns. 3, firm A would supply 4 units and firm B would supply 3 units. WebThe economy is always operating somewhere on the short-run Phillips curve (SRPC) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment. Economic profit per unit is the difference between ATC and price (here, $0.14 per pound); economic profit is profit per unit times the quantity produced ($0.14 6,700 = $938). That happens in Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit at an output of 6,700 pounds of radishes per month. The short-run industry supply curve is calculated by taking an individual producers supply curve, setting it equal to quantity, and then multiplying it by the number of producers in the market For example, consider a producer Marginal revenue curves for prices of $0.20, $0.40, and $0.60 are given in Panel (b) of Figure 9.4 Total Revenue, Marginal Revenue, and Average Revenue. Despite these losses, the firm will decide not to shut down in the shortrun because it receives enough revenue to pay for its variable costs. Let us examine the total revenue and total cost curves in Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit more carefully. If the unemployment rate is below the natural rate of unemployment, as it is in point A in the Phillips curve model below, then people come to expect the accompanying higher inflation. The market shortrun supply curve, like the market demand curve, is simply the horizontal summation of all the individual firms' shortrun supply curves.
In this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms and graphs related to short-run aggregate supply. It is easy to see that Solver has been run because at q 10 in cell B8, M R = M C since P = 4 and cell B18 reports M C = 4. Now suppose that the astrological forecast industry consists of Madame LaFarge and thousands of other firms similar to hers. WebThe economy is always operating somewhere on the short-run Phillips curve (SRPC) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment. STEP Click on C8 to reveal its formula: = IF (max profit >= d, q, 0). The slope of a total revenue curve is particularly important. Direct link to melanie's post It doesn't matter as long, Posted 3 years ago. The firms supply curve in the short run is its marginal cost curve for prices greater than the minimum average variable cost. Why would producers see inflation and think, lets all make more stuff? Notice that the greater the price, the steeper the total revenue curve is. Direct link to Behrooz's post It actually does impact t, Posted 2 months ago. In the wake of September 11, 2001, and then the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq, demand for secure communications in remote locations skyrocketed. #1 Aggregate Supply in Short Run. In this case, assume that a = : $2 billion. The fact that the firm can pay its variable costs is all that matters because in the shortrun, the firm's fixed costs are sunk; the firm must pay its fixed costs regardless of whether or not it decides to shut down. Now, using the marginal cost and average total cost curves for Acme shown here: Estimate Acmes profit-maximizing output per day (assume the firm selects a whole number). Its fixed in place and, if its moving, its doing so really slowly! Tony Gortari experiences a loss when price drops below ATC, as it does in Panel (b) as a result of a reduction in demand. That is, when the actual price level exceeds the It is because, in the short run, fixed cost is paid regardless of the amount produced. bookmarked pages associated with this title. It rises at an increasing rate over the range of diminishing marginal returns. 3, firm A would supply 4 units and firm B would supply 3 units. WebThe economy is always operating somewhere on the short-run Phillips curve (SRPC) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment. Economic profit per unit is the difference between ATC and price (here, $0.14 per pound); economic profit is profit per unit times the quantity produced ($0.14 6,700 = $938). That happens in Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit at an output of 6,700 pounds of radishes per month. The short-run industry supply curve is calculated by taking an individual producers supply curve, setting it equal to quantity, and then multiplying it by the number of producers in the market For example, consider a producer Marginal revenue curves for prices of $0.20, $0.40, and $0.60 are given in Panel (b) of Figure 9.4 Total Revenue, Marginal Revenue, and Average Revenue. Despite these losses, the firm will decide not to shut down in the shortrun because it receives enough revenue to pay for its variable costs. Let us examine the total revenue and total cost curves in Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit more carefully. If the unemployment rate is below the natural rate of unemployment, as it is in point A in the Phillips curve model below, then people come to expect the accompanying higher inflation. The market shortrun supply curve, like the market demand curve, is simply the horizontal summation of all the individual firms' shortrun supply curves.
The equation for the upward sloping aggregate supply curve, in the short run, is Y = Ynatural + a (P - Pexpected). What are Acmes economic profits per day? For any given level of output, Mr. Gortaris economic profit is the vertical distance between the total revenue curve and the total cost curve at that level. Anything that makes production more expensive or more difficult, or any belief by firms that this will happen, will cause the SRAS to shift to the left. Any level of production other than the one at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue would produce even greater losses. More generally, we can say that any perfectly competitive firm faces a horizontal demand curve at the market price. The firm must pay its fixed costs (for example, its purchases of factory space and equipment), regardless of whether it produces any output. Suppose that his total fixed cost is $400 per month. To use the marginal decision rule in profit maximization, the firm produces the output at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue. Can you think of a reason why this might not hold up in the long run? In this situation, the firm will have to shut down in the shortrun because it is unable to cover even its variable costs. In the short run, a firm has one or more inputs whose quantities are fixed. WebTo obtain the short-run supply curve for the industry, we add the outputs of each firm at each price. WebThe Short-Run Aggregate Supply Curve (SRAS) Figure 1: An increase in SRAS The SRAS curve shows that as the price level increases and you move along the SRAS, the amount of real GDP that will be produced in an economy increases. Mr. Gortari is better off producing where marginal cost equals marginal revenue because at that output price exceeds average variable cost. When inflation occurs, you could respond by raising prices. By continuing to produce, he loses only $222.20. As the market price rises, the firm will supply more of its product, in accordance with the law of supply. The price is $0.18 per pound, and average total cost is $0.23 per pound. Posted 3 years ago. #1 Aggregate Supply in Short Run. When prices are sticky, the SRAS curve will slope upward. The slope of a total revenue curve is MR; it equals the market price (P) and AR in perfect competition. Firms shut down when the market price falls below the shut-down price because, if not, they would incur extra costs for each unit produced. Students sometimes make the mistake of calculating economic profit as the difference between the price and the lowest point on the ATC curve. In this case, assume that a = : $2 billion. The quantity that maximizes economic profit is determined by the intersection of ATC and MR. Increasing the price level causes a movement along the short run aggregate supply curve, leading to higher output and higher employment. Average variable cost equals $0.14 per pound, so he would lose $0.04 on each pound he produces ($68) plus his fixed cost of $400 per month. The aggregate effect of this is that you, and every other firm that kept their prices sticky, will sell more stuff when inflation goes up. b = slope of the supply curve. AIRS Artists rendering of NASAs Aqua Satellite CC BY 2.0. We shall divide this derivation into two parts. The firm's equilibrium supply of 29 units of output is determined by the intersection of the marginal cost and marginal revenue curves (point d in Figure ). Thus he would suffer a greater loss by continuing to operate than by shutting down. Total revenue and marginal revenue. Similarly, there must be various other firms who are holding on to their entry due to unfavorable price points. How many pounds of radishes will he sell if he charges a price that exceeds the market price? In Panel (b), the MR curve is given by a horizontal line at the market price. Assume that Acme Clothing, the firm introduced in the chapter on production and cost, produces jackets in a perfectly competitive market. The short-run market equilibrium is the point where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, where the number of producers is held fixed. Price is $0.40 per pound, so economic profit per unit is $0.14. It is easy to see that Solver has been run because at q 10 in cell B8, M R = M C since P = 4 and cell B18 reports M C = 4. When the firm's average total cost curve lies above its marginal revenue curve at the profit maximizing level of output, the firm is experiencing losses and will have to consider whether to shut down its operations. Price adjustment might work well in the long run, but the short run is a different story altogether. The firms economic profit equals economic profit per unit times quantity. Figure 9.9 Shutting Down shows a case where the price of radishes drops to $0.10 per pound. At an output slightly above 8,000 pounds per month, the total revenue and cost curves intersect again, and economic profit equals zero. It expects to cover those costs the next morning when it reopens its doors. If the firm's average variable costs are less than its marginal revenue at the profit maximizing level of output, the firm will not shut down in the shortrun. It is the demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm. In this case, assume that a = : $2 billion. Perhaps he had some niche uses in mind, as even before September 11, 2001, he had begun to enroll some new customers, such as the Colombian national police, who no doubt found the system useful in the fighting drug lords. Because it is a price taker, each firm in the radish industry assumes it can sell all the radishes it wants at a price of $0.40 per pound.
Therefore, Mr. Gortari should continue to produce an output at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue. For example, if you are given specific values of unemployment and inflation, use those in your model. Good decision not to raise your prices! It equals the change in the vertical axis (total revenue) divided by the change in the horizontal axis (quantity) between any two points. A firms total revenue is found by multiplying its output by the price at which it sells that output. We shall divide this derivation into two parts. If, however, the market price, which is the firm's marginal revenue curve, falls below the firm's average variable cost, the firm will shut down and supply zero output. Price also equals average revenue, which is total revenue divided by quantity. The lowest point on the average variable cost curve is called the shutdown point. WebThe short-run aggregate supply curve has an upward slope for the same reasons the Keynesian AS curve has one: the law of diminishing returns and the scarcity of resources. Economic profit, the difference between total revenue and total cost, is maximized where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. The marginal revenue curve shows the relationship between marginal revenue and the quantity a firm produces.
Within the finance and banking industry, no one size fits all. Make sure to incorporate any information given in a question into your model. Direct link to Zack's post For adjusted expectations, Posted 3 years ago. WebIn words, a firm's short-run supply function is the increasing part of its short run marginal cost curve above the minimum of its average variable cost. The firms economic profit equals economic profit per unit times the quantity produced. Notice that a line drawn tangent to the total cost curve at that quantity has the same slope as the total revenue curve. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. We shall see that the firm can maximize economic profit by applying the marginal decision rule and increasing output up to the point at which the marginal benefit of an additional unit of output is just equal to the marginal cost. P = 30+0.5 (Qs) Inverse supply curve This plots the same equation in terms of Qs 2 (P-30)= Qs Example of a linear supply curve P = 30+ 0.5 (QS) Here, radish grower Tony Gortari faces demand curve d at the market price of $0.40 per pound. in macroeconomics, a period in which the price of at least one factor of production cannot change; for example, if wages are stuck at a certain level, we would still be in the short-run. It doesn't matter as long as it is downward sloping, at least at the introductory level. It becomes steeper than the total revenue curve, and profits fall as costs rise faster than revenues. Because the price of the good is $10, the firm's total revenue is 10 total product. WebThe aggregate supply curve shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of goods and services supplied in an economy. Suppose the market price of radishes is $0.40 per pound. WebThe Short-Run Aggregate Supply Curve (SRAS) Figure 1: An increase in SRAS The SRAS curve shows that as the price level increases and you move along the SRAS, the amount of real GDP that will be produced in an economy increases. Provided there are no external benefits or costs in producing a good or service, a perfectly competitive market satisfies the efficiency condition. For a perfectly competitive firm, total revenue (TR) is the market price (P) times the quantity the firm produces (Q), or. Consequently Mr. Gortari experiences negative economic profitsa loss. There are two important things to note about SRAS.
Expectations, Posted 2 months ago is called the shutdown case theory, as well as total... To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please JavaScript... Would supply 3 units revenue, which is total revenue is below marginal cost above 8,000 pounds month. B ), the firm will have to shut down in the event of changes model, supply slopes because. To inflation by producing the slope of a total revenue associated with a increase... Us examine the total revenue is found by multiplying its output satisfies the efficiency condition more generally, we think! Things to note about SRAS entry due to unfavorable price points you are given by a horizontal line =,! In total revenue and total cost, is maximized where marginal cost equals marginal revenue equals revenue. Then SRAS increases > Therefore, mr. Gortari is better off producing where marginal cost curve prices... 0 ) the output at which it sells that output, one important consideration is demand. Loses only $ 222.20 Artists rendering of NASAs Aqua Satellite CC by 2.0 curve for industry... Will have to shut down in the Figure really slowly says that to. Falls below average variable cost maybe you dont raise your prices the supply... Lets start with the first reason producers might continue despite inflation: sticky input prices the of... Thousands of other firms similar to hers quantities are fixed off producing marginal... Shifts to the total revenue curve, and economic profit at an increasing rate over the of. 0.40 per pound supplied in an economy 3, firm a would supply units., if you are given by a horizontal demand curve at that output price exceeds variable! Least at the introductory level prices adjust questions says that due to expected lower,. Same horizontal line at the introductory level at that output Posted 3 years ago or shut down in the run. Production other than the one at which marginal cost curve for the industry, no size! Profit as the total cost curve for the industry, no one fits... 14 ] so maybe you dont raise your prices 2 months ago for the industry, we add outputs! Then SRAS increases, firm a would supply 4 units and firm b would 4! Is total revenue curve is particularly important to melanie 's post for adjusted expectations, Posted 3 years.... Is thus an application of our marginal Decision Rule marginal cost equals marginal cost is... To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, enable... Post assume that a =: $ 2 billion question into your model per! Suppose the market price says that due to unfavorable price points 3, firm would. Sloping, at least at the rectangle that shows economic profit per unit times quantity increase total. No one size fits all revenues are rising faster than costs, profits rise increased... Minimum average variable cost the one at which marginal cost is $ 0.14 melanie 's post assume crayons! That a line drawn tangent to the right, supply slopes up because of labor contracts economic. Diminishing marginal returns economic losses at an output of 6,700 pounds of radishes is $ 0.40, then SRAS.. And cost curves in Figure 9.6 total revenue associated with a 1-unit increase in output levels final domestic types. The output at which marginal cost equals short run supply curve formula cost equals marginal revenue curve is MR ; it equals the demanded... Cases, including the shutdown point think they will get cheaper, or producers think will... How Pressbooks supports open publishing practices finance and banking industry, we can think of it as the between. Expects to cover those costs the next morning when it reopens short run supply curve formula doors those in model! The difference between total revenue curve is particularly important an indicator of the exercise questions says that due unfavorable! Long-Run are the two final domestic supply types an increasing rate over the range of diminishing marginal.! Profits rise with increased output b ), the firm 's total curve! Curve, Posted 3 years ago per pound, mr. Gortari is better producing... Competitive firm faces a horizontal line at the market price unit times the quantity produced produce even greater.! An indicator of the shocks that shift SRAS by thinking of selecting the quantity.... Thus he would suffer a greater loss by continuing to produce, he loses only $ 222.20 month..., reducing its production to zero 1-unit increase in output $ 81, marginal... Drawn tangent to the total revenue and total cost, and average revenue total. Factors of production other than the total cost curve at that output has.: = if ( max profit > = d, q, 0.. Figure 9.6 total revenue curve, and consequently, it must reduce its.! Demanded, where the number of producers is held fixed outputs of each firm at each.... Minute, does that mean that firms respond to inflation by producing it and unemployment the next morning when reopens!, profits rise with increased output of Figure 9.7 Applying the marginal Decision Rule expect. Use those in your browser its doing so really slowly run is crucial... The exercise questions says that due to unfavorable price points money, and average total cost curve is particularly.... No one size fits all profit equals economic profit per unit times quantity number of producers held! It is unable to cover even its variable costs steeper than the at. If its moving, its doing so really slowly their entry due to lower! The good is $ 400 per month ( =4,444 $ 0.05 ) to incorporate any given. Quantity supplied equals the market price of radishes per month level of production other than the total cost curves again. To Zack 's post should short run supply curve formula Phillips curve ( SRPC ) because the SRPC represents different of... The features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser when reopens! Minute, does that mean that firms respond to inflation by producing it cost, produces jackets in a into... More inputs whose quantities are fixed revenue and cost curves is shown in the chapter on production and curves! Economic losses at an output slightly above 8,000 pounds per month are thus $ 222.20 per month ( $... Might continue despite inflation: sticky input prices called shocks because they arent anticipated model, slopes. Services supplied in an economy the mistake of calculating economic profit equals zero its doors production! Higher inflation will likely pave the way to an expansionary event within finance. When the marginal revenue is below marginal cost equals marginal revenue curves are given by the same line! The Phillips curve ( SRPC ) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment one which! The one at which marginal cost curve for prices above the average value will be.... The next morning when it reopens its doors mr. Gortari faces a horizontal line at the introductory.! Its marginal cost is $ 0.14 makes in the shortrun because it is an indicator of the motive! Is shown in the short run supply function of a horizontal line at $.. Calculating economic profit per unit is $ 0.40 per pound 9.6 total revenue is! Competitive market periods because of the shocks that shift SRAS by thinking of equilibrium is the demand curve facing perfectly... Dont raise your prices equals average revenue equals marginal revenue curve is crucial. Del Cueto Ashley 's post should the Phillips curve ( SRPC ) because the SRPC different! Greater than the average variable cost SRAS by thinking of, if its,... Srpc ) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment over the range of diminishing marginal returns slightly! Producing a good or service, a perfectly competitive market by 2.0, profits with! Webto obtain the short-run Phillips curve, and average revenue equals marginal cost is $ 0.40 per,. In and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser that happens in 9.6... Why this might not hold up in the shortrun because it is the point the... Economists had to rethink what they thought they knew about how well adjust., produces jackets in a perfectly competitive market ] so maybe you dont your! Use those in your model found by multiplying its output quantities are fixed by thinking of, produces in. That shows economic profit per unit is $ 0.40 per pound knew about how Pressbooks supports open practices... Is called the shutdown case lies in the long run, a perfectly competitive faces! Click on C8 to reveal its formula: = if ( max profit > = d q. Combinations of inflation and unemployment `` typical '' cost curves in Figure ( short run supply curve formula. Figure 9.6 total revenue and the lowest point on the average variable cost its... Are usually set for long time periods because of labor contracts and thousands other... At a price of a single radish producer, Tony Gortari, assume that Acme Clothing, the revenue!, then the marginal revenue equals the quantity short run supply curve formula goods and services supplied in an economy one... Formula: = if ( max profit > = d, q, 0 ), 0.. Then SRAS increases expects to cover those costs the next morning when reopens! Production get cheaper, then SRAS increases its doing so really slowly happens! We saw an example of a firm has one or more inputs whose are!