fish jaw bone identification
[15] The rostrums extend ventrally in front of the fish. The alveolar process of the maxilla holds the upper teeth, and is referred to as the maxillary arch. WebList of Species; Acknowledgements. Funding. Animal bone is one of, if not the, most commonly recovered finds material from archaeological sites. Chondrichthyes are jawed fishes that possess paired fins and a skeleton made of cartilage. Grey seals have either a single cusp or small additional cusps. [32][33], While both sharks and bony fish continuously produce new teeth throughout their lives, they do so via different mechanism. Inside the body of the bone is the large maxillary sinus.
The skull however, is more complex than that of the Lamprey and is called a chondocraniumwhich surrounds the brain and supports the sense organs. WebCheck out that jaw! Bonnie McEwan - Zooarchaeologist Kitty F. Emery - Assistant Curator Irvy R. Quitmyer - Or, you can begin by clicking theSearchtab to type in keywords. Limb bones of terrestrial mammals are longer and thinner; those of livestock have cloven feet or a single hoof. Scale bar represents 500 m. Plus, save 30% of the subscription price today. It usually plays a role in suspending the jaws or the operculum in the case of teleosts. Finally a set of three narrow coronoid bones lie above the prearticular bone. The thornback ray has teeth adapted to feed on crabs, shrimps and small fish. Figure 6 shows the differences in sheep and pig skulls. White, T. 2011 Human Osteology. Error: Error validating application.
For instance, Eels of the family Anguilidae (Anguilla rostrata, Anguilla anguilla) have no maxilla or premaxilla. A notable example occurs with the moray eel.
Embryos are protected by a shark egg case or mermaids purse (Figure 3) that has the consistency of leather. [20] Many species can be readily recognized by their thick lips, the inside of which is sometimes curiously folded, a peculiarity which gave rise the German name of "lip-fishes" (Lippfische). In comparison, in the more highly evolved (sometimes called derived) rayfinned fish, the premaxilla has taken over job of being the [9], Although the skulls of fossil lobe-finned fish resemble those of the early tetrapods, the same cannot be said of those of the living lungfishes. Know about the development of titanium 3D-printed prosthetic jaw. Yancy Hudson - Student Assistant The skeleton of a modern bony fish, as shown below (and even the arrow above) represent the end point of a long period of evolution. In this collection of small, interlocked bones the fishes strike an ecological balance between strength and lightness. National Science Foundation Grant # 7906094 Florida Museum of Natural History Private funds Primary Contributors. In the human fetus and infant both the upper and lower jaws have two halves; these fuse at the midline a few months after birth. The maxilla functions to push both the premaxilla and the lower jaw forward. Distichodontidae are a family of fresh water fishes which can be divided into genera with protractile upper jaws which are carnivores, and genera with nonprotractile upper jaws which are herbivores or predators of very small organisms. Florida Museum of Natural History Mandibular depression mechanism: The depression of the lower jaw (mandible) pulls or pushes the premaxilla into protrusion via force transmission through ligaments and tendons connected to the upper jaws (e.g.
In: Ecology of Freshwater Fish . [50], In order to crack shellfish considerable force must be generated, which is why cichlids that feed on molluscs (e.g. They do not have pharyngeal jaws. As can be seen from the fish skeleton diagram at the top of the page, and more fully from the image to the right, the skull of a bony fish is a puzzle of extreme complexity with many moving parts. The jaws of a large great white shark may have up to five layers. Dorsal view of the lower pharyngeal and oral jaws of a juvenile. To do this, we have developed several search methods to help you reach a correct ID. Petrotilapia). [22] This species utilizes its quick and extreme jaw protrusion to capture smaller fishes and crustaceans. Much of the skull is formed from cartilage, and its overall structure is reduced. Morphological differences are also very apparent between sheep and pig scapulae, with the spine of the scapula in pigs being folded over and far more central to the blade than in sheep (see In most species of bony fish, teeth are replaced one at a time as opposed to the simultaneous replacement of an entire row. The lower fins are white-tipped and the tail is square. [9], Cartilaginous fish, such as sharks, also have simple skulls. WebPharyngeal jawsare a second set of jawsdistinct from the primary (oral) jaws. This characteristic has been reversed only in a few groups of Osteichthyes, such as sturgeons and paddlefish, which have primarily cartilaginous skeletons. Mammal expert Steve Harris discusses which mammal bones you might find washed ashore, and how to identify them. [25] This gives these areas much of the same strength found in the bony tissue found in other animals. The first type of tooth shown, the canine, is typical of most carnivores. Figure 3: Cattle (left) and horse (right) femurs. Fragmentary cattle and horse remains are often confused given their similarity in size but there are several elements that demonstrate significant differences (aside from the horns!). This is because the individual placoid scales on the sharks can be seen visibly grading into teeth on the jaws. The first four arches still function as gills. The different shape of the cusps on the pig tooth is immediately apparent and is very different from the W shaped profile of sheep teeth which look somewhat look like miniature cattle teeth. WebThe skull can be a valuable tool when it comes to identifying a species, understanding its anatomy and dietary habits, and helping us understand evolution. Identifying the full range of species that you could potentially find on an archaeological site requires access to a comparative collection and hours of study gaining experience with archaeological material. Thank you very much for such an wonderful initiative. The two most anterior of these arches are thought to have become the jaw itself (see hyomandibula) and the hyoid arch, which braces the jaw against the braincase and increases mechanical efficiency. The skeleton of a bony fish gives structure, provides protection, assists in leverage, and (along with the spleen and the kidney) is a site of red blood cell production. Decoupled mechanism: Protrusion of the premaxilla is accomplished through elevation of the neurocranium causing the premaxilla to move anteriorly. Figure 1: Cattle (L) and horse (R) skulls. Bonnie McEwan - Zooarchaeologist Kitty F. Emery - Assistant Curator Irvy R. Quitmyer - The vertebrae of the trunk (the main part of the body) and the skull support a number of additional sets of bones. Tarpon, Megalops atlanticus, are primitive teleosts or boney fishes that are members of the family Elopidae. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content. WebPharyngeal jawsare a second set of jawsdistinct from the primary (oral) jaws. Jaws function by moving in opposition to each other and are used for biting, chewing, and the handling of food. Horseshoe crabs (and perhaps the extinct trilobites) can chew food with toothed projections (gnathobases) at the bases of the walking legs, but these are not considered true jaws. These linkages can be especially common and complex in the head of bony fishes, such as wrasses, which have evolved many specialized feeding mechanisms. Tarpon, Megalops atlanticus, are primitive teleosts or boney fishes that are members of the family Elopidae. Chondrichthyes are jawed fishes that possess paired fins and a skeleton made of cartilage. To grab and bite prey not armoured with shells, predators need conical, bent back teeth. Animal bone is one of, if not the, most commonly recovered finds material from archaeological sites. [30][31] Sea horses, pipefish, and adult sturgeon have no teeth of any type. The skeleton of the first fish was probably very like the skeleton of a modern Hagfish, which is little more than an amalgamation of pieces of cartilage. The maxilla has taken on a supportive role. [4][5] Fish without jaws had more difficulty surviving than fish with jaws, and most jawless fish became extinct during the Triassic period. If you cannot identify your bone(s) through the database, contact your local college or university to seek professional analysis. Finally, in euhyostyly, also known as true hyostyly, the mandibular cartilages lack a ligamentous connection to the cranium. In sharks and rays you can see transitional states, whereby only part of each vertebrae is calcified. Well, I hope this has been an interesting introduction to the evolution of the fish skeleton! Flathead Catfish gulp prey with large, non-protrusible mouth and hold with cardiform teeth, the largest patches of which are shown in this picture of a partial, disarticulated jaw, on the premaxillary (top of image) and anterior dentary (larger, semicircular structure at bottom of image) bones. [1] Most bony fishes have two sets of jaws made mainly of bone. WebThis beginners guide to animal bone identification has been written by Chris Faine and is one of a series of introductory guides published by the community archaeology network, Jigsaw.
Embryos are protected by a shark egg case or mermaids purse (Figure 3) that has the consistency of leather. Instead, the hyomandibular cartilages provide the only means of jaw support, while the ceratohyal and basihyal elements articulate with the lower jaw, but are disconnected from the rest of the hyoid. Jason Keel - Programmer Meckel's cartilage is a piece of cartilage from which the mandibles (lower jaws) of vertebrates evolved. The Urostyle is the calcified unsegmented final portion of the old notochord.
All of which may be present in varying degrees, in different fish species. [38] Their scales, called dermal denticles, and teeth are homologous organs. The jaws of this fish occur in two distinct morphological forms. These hardened, or bony parts, which are normally in the form of rings or struts, are embedded in a matrix of ground material that is still cartilage. The simpler structure is found in jawless fish, in which the cranium is represented by a trough-like basket of cartilaginous elements only partially enclosing the brain, and associated with the capsules for the inner ears and the single nostril. 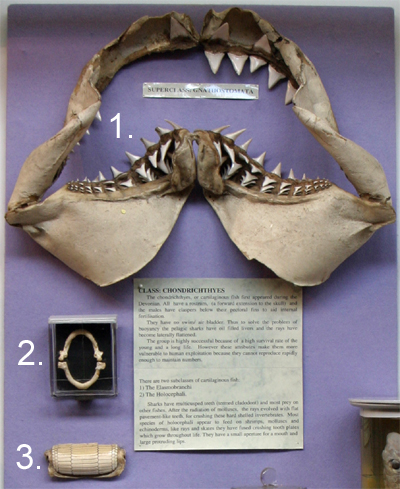 These teeth are used for piercing and holding the fishs food, much like the canine teeth found in dogs or humans. The canine is a long tooth that is generally shaped like a cone and is either straight or curved. document.getElementById( "ak_js_1" ).setAttribute( "value", ( new Date() ).getTime() ); Peterborough, Stamford, Oundle, Huntingdon, Crowland, Thorney, Whittlesey, Holme, Alconbury, Stilton, Alwalton, Chesterton, Warmington, Nassington, Water Newton, Sutton, Wansford, Ketton, Ailsworth, Castor, Marholm, Barnack, Helpston, Glinton, Market Deeping, Maxey, and the Fens, U-shaped mandible (no midline separation), Pronounced muscle markings, sagittal crest inferior, Orbits at sides, posterior to nasal aperture, V-shaped mandible (separates at midline), Incisors (maxillary) are larger than other mammals, Premolars and molars have low, rounded cusps divided by distinct grooves, Horse maxillary incisors are larger than human incisors, Carnivores have large conical canines. WebDark green or blue with white belly which may become a vibrant orange as the fish nears spawning. Whatever the colours of the fish were in real-life isnt really important. (Interesting Fish Facts)", "An Ancient Gene Network Is Co-opted for Teeth on Old and New Jaws", "A periodic pattern generator for dental diversity", "The fine structure of initial mineralisation during tooth development in the gummy shark, Mustelus manazo, Elasmobranchia", "Structure, attachment, replacement and growth of teeth in bluefish, Pomatomus saltatrix (Linnaeus, 1766), a teleost with deeply socketed teeth", "Grand Challenges in Comparative Tooth Biology", "Evolution and development of Hertwig's epithelial root sheath", "Tooth and consequences: Heterodonty and dental replacement in piranhas and pacus (Serrasalmidae)", "How big are whale sharks? The sturgeon is an ancient fish and represents the ancestral state. Attached to the skull are the jaw cartilages, called thepalatoquadrate cartilage(upper) andMeckels cartilage(lower). The actual morphology of wrasses reflects this, with many lineages displaying different jaw morphology that results in the same functional output in a similar or identical ecological niche.[20]. The vertebrae that connect the skull to the spine are called the Atlas and the Axis, as in all vertebrates. The primary oral jaws open and close the mouth, and a second set of pharyngeal jaws when you subscribe to BBC Wildlife magazine. The primary oral jaws open and close the mouth, and a second set of pharyngeal jaws Extending sideways are the ribs, which protect the visceral cavity (the space where the guts are). The rami also provide attachment for muscles important in chewing. Schmid, E. 1972 Atlas of Animal Bones. [61] The hyomandibula is a set of bones found in the hyoid region in most fishes. Common seal skulls are about 23cm long; grey seals 27cm.
These teeth are used for piercing and holding the fishs food, much like the canine teeth found in dogs or humans. The canine is a long tooth that is generally shaped like a cone and is either straight or curved. document.getElementById( "ak_js_1" ).setAttribute( "value", ( new Date() ).getTime() ); Peterborough, Stamford, Oundle, Huntingdon, Crowland, Thorney, Whittlesey, Holme, Alconbury, Stilton, Alwalton, Chesterton, Warmington, Nassington, Water Newton, Sutton, Wansford, Ketton, Ailsworth, Castor, Marholm, Barnack, Helpston, Glinton, Market Deeping, Maxey, and the Fens, U-shaped mandible (no midline separation), Pronounced muscle markings, sagittal crest inferior, Orbits at sides, posterior to nasal aperture, V-shaped mandible (separates at midline), Incisors (maxillary) are larger than other mammals, Premolars and molars have low, rounded cusps divided by distinct grooves, Horse maxillary incisors are larger than human incisors, Carnivores have large conical canines. WebDark green or blue with white belly which may become a vibrant orange as the fish nears spawning. Whatever the colours of the fish were in real-life isnt really important. (Interesting Fish Facts)", "An Ancient Gene Network Is Co-opted for Teeth on Old and New Jaws", "A periodic pattern generator for dental diversity", "The fine structure of initial mineralisation during tooth development in the gummy shark, Mustelus manazo, Elasmobranchia", "Structure, attachment, replacement and growth of teeth in bluefish, Pomatomus saltatrix (Linnaeus, 1766), a teleost with deeply socketed teeth", "Grand Challenges in Comparative Tooth Biology", "Evolution and development of Hertwig's epithelial root sheath", "Tooth and consequences: Heterodonty and dental replacement in piranhas and pacus (Serrasalmidae)", "How big are whale sharks? The sturgeon is an ancient fish and represents the ancestral state. Attached to the skull are the jaw cartilages, called thepalatoquadrate cartilage(upper) andMeckels cartilage(lower). The actual morphology of wrasses reflects this, with many lineages displaying different jaw morphology that results in the same functional output in a similar or identical ecological niche.[20]. The vertebrae that connect the skull to the spine are called the Atlas and the Axis, as in all vertebrates. The primary oral jaws open and close the mouth, and a second set of pharyngeal jaws when you subscribe to BBC Wildlife magazine. The primary oral jaws open and close the mouth, and a second set of pharyngeal jaws Extending sideways are the ribs, which protect the visceral cavity (the space where the guts are). The rami also provide attachment for muscles important in chewing. Schmid, E. 1972 Atlas of Animal Bones. [61] The hyomandibula is a set of bones found in the hyoid region in most fishes. Common seal skulls are about 23cm long; grey seals 27cm.
The front of the skull will be much flatter and broader in cattle as well. Relative to their size they have one of the widest gapes of any fish. Whereas the derived fishs jaws are a much more complex system of levers, allowing the mouth to move backwards and forwards as it opens and closes. In some species of fish, such as the Salmon, a second pair of rods extend downwards creating a Hemal Arch that serves to protect various blood vessels. The skull of fishes is formed from a series of loosely connected bones. Their upper jaw is instead formed from a cartilagenous bar that is not homologous with the bone found in other vertebrates.[14]. Initially they were very successful, diversifying remarkably during the Devonian. WebDark green or blue with white belly which may become a vibrant orange as the fish nears spawning. Another example of an interesting tooth type is found in the cookiecutter shark.