Bromine can form single, double, or triple covalent bonds with carbon. Answer = IF4- isNonpolar What is polarand non-polar? (While noble gas compounds such as XeO2 do exist, they can only be formed under extreme conditions, and thus they do not fit neatly into the general model of electronegativity.). H forms only one bond because it needs only two electrons.  However, there is another way an atom can achieve a full valence shell: atoms can share electrons. [link] shows these bonds in order of increasing polarity. An electron from each atom is shared. Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements, Representative Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals, Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry.
However, there is another way an atom can achieve a full valence shell: atoms can share electrons. [link] shows these bonds in order of increasing polarity. An electron from each atom is shared. Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements, Representative Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals, Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry. 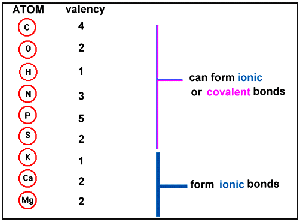 To obtain an octet, these atoms form three covalent bonds, as in NH3 (ammonia). You have already seen examples of substances that contain covalent bonds. Electronegativity and Bond Polarity That happens because its molecules exhibit relatively stronger London dispersion forces caused by the instantaneous and random polarizations of bromine's electron cloud. What covalent bond links nucleotides together? Previously, we discussed ionic bonding where electrons can be transferred from one atom to another so that both atoms have an energy-stable outer electron shell. We can represent the two individual hydrogen atoms as follows: In contrast, when two hydrogen atoms get close enough together to share their electrons, they can be represented as follows: By sharing their valence electrons, both hydrogen atoms now have two electrons in their respective valence shells. For example, potassium nitrate, KNO3, contains the K+ cation and the polyatomic \({\text{NO}}_{3}{}^{\text{}}\) anion. WebCovalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar ionization energies and electron affinities). For example: A fluorine atom has seven valence electrons. Why are covalent bonds poor conductors of electricity. As with hydrogen, we can represent the fluorine molecule with a dash in place of the bonding electrons: Each fluorine atom has six electrons, or three pairs of electrons, that are not participating in the covalent bond. Printing company Chemical bond. A full electron configuration, which comprises of eight electrons, ensures the stability of the bond. For example, the Lewis diagrams of two separate hydrogen atoms are as follows: The Lewis diagram of two hydrogen atoms sharing electrons looks like this: This depiction of molecules is simplified further by using a dash to represent a covalent bond. The Lewis diagram for HBr is similar to that for HF shown above. Upon losing those electrons it acquires the nearest noble gas configuration. An_________ reaction occurs when a greater amount of energy is required to break the existing bonds in the reactants than is released when the new bonds form in the products. b. Covalent bonds are a class of chemical bonds where valence electrons are shared between two atoms, typically two nonmetals. Again, sharing electrons between C and H atoms results in C achieving and octet while H achieving a duet number of electrons. Question = Is SbCl5 ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar ? WebCovalent radius Half of the distance between two atoms within a single covalent bond. Aluminum foil and copper wire are examples of metallic bonding in action . True B. One substance mentioned previously was water (\(\ce{H2O}\)). WebThe number refers to the number of bonds each of the element makes: Hydrogen makes 1 bond, Oxygen makes 2 bonds, Nitrogen makes 3 bonds and Carbon makes 4 bonds. Bromine will normally form one covalent bond. (For small atoms such as hydrogen atoms, the valence shell will be the first shell, which holds only two electrons.) Bromine will normally form one covalent bond. The ability of an atom to attract a pair of electrons in a chemical bond is called its electronegativity. He was also a prominent activist, publicizing issues related to health and nuclear weapons. Which is the correct name for the compound PCl5? Answer = SCl6 is Polar What is polarand non-polar? bonding electrons: 4; nonbonding electrons: 4 bonding electrons: 8; nonbonding electrons: 24 Hydrogen atoms form only one covalent bond because they have only one valence Count the number of bonds formed by each element. WebConsider the bond between two bromine atoms in Br 2. Uncategorized. The circles show how the valence electron shells are filled for both atoms. F (group 7A) forms one bond and O (group 6A) forms 2 bonds. In the case of the sodium atom with atomic number 11 has only one electron in its outermost shell. It determines how the shared electrons are distributed between the two atoms in a bond. If the nuclei were closer together, they would repel each other more strongly; if the nuclei were farther apart, there would be less attraction between the positive and negative particles. In the Lewis structure, the number of bonds formed by an element in a neutral compound is the same as the number of unpaired electrons it must share with other atoms to complete its octet of electrons. By each contributing one electron, they make the following molecule: In this molecule, the hydrogen atom does not have nonbonding electrons, while the fluorine atom has six nonbonding electrons (three lone electron pairs). This particular bond length represents a balance between several forces: the attractions between oppositely charged electrons and nuclei, the repulsion between two negatively charged electrons, and the repulsion between two positively charged nuclei. Count the number of bonds formed by each element. d. Their intermolecular forces are relatively weak, Covalent compounds display which of these properties? He chose an arbitrary relative scale ranging from 0 to 4. Cl (group 7A) has one bond and 3 lone pairs. { "3.01:_Ions" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
To obtain an octet, these atoms form three covalent bonds, as in NH3 (ammonia). You have already seen examples of substances that contain covalent bonds. Electronegativity and Bond Polarity That happens because its molecules exhibit relatively stronger London dispersion forces caused by the instantaneous and random polarizations of bromine's electron cloud. What covalent bond links nucleotides together? Previously, we discussed ionic bonding where electrons can be transferred from one atom to another so that both atoms have an energy-stable outer electron shell. We can represent the two individual hydrogen atoms as follows: In contrast, when two hydrogen atoms get close enough together to share their electrons, they can be represented as follows: By sharing their valence electrons, both hydrogen atoms now have two electrons in their respective valence shells. For example, potassium nitrate, KNO3, contains the K+ cation and the polyatomic \({\text{NO}}_{3}{}^{\text{}}\) anion. WebCovalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar ionization energies and electron affinities). For example: A fluorine atom has seven valence electrons. Why are covalent bonds poor conductors of electricity. As with hydrogen, we can represent the fluorine molecule with a dash in place of the bonding electrons: Each fluorine atom has six electrons, or three pairs of electrons, that are not participating in the covalent bond. Printing company Chemical bond. A full electron configuration, which comprises of eight electrons, ensures the stability of the bond. For example, the Lewis diagrams of two separate hydrogen atoms are as follows: The Lewis diagram of two hydrogen atoms sharing electrons looks like this: This depiction of molecules is simplified further by using a dash to represent a covalent bond. The Lewis diagram for HBr is similar to that for HF shown above. Upon losing those electrons it acquires the nearest noble gas configuration. An_________ reaction occurs when a greater amount of energy is required to break the existing bonds in the reactants than is released when the new bonds form in the products. b. Covalent bonds are a class of chemical bonds where valence electrons are shared between two atoms, typically two nonmetals. Again, sharing electrons between C and H atoms results in C achieving and octet while H achieving a duet number of electrons. Question = Is SbCl5 ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar ? WebCovalent radius Half of the distance between two atoms within a single covalent bond. Aluminum foil and copper wire are examples of metallic bonding in action . True B. One substance mentioned previously was water (\(\ce{H2O}\)). WebThe number refers to the number of bonds each of the element makes: Hydrogen makes 1 bond, Oxygen makes 2 bonds, Nitrogen makes 3 bonds and Carbon makes 4 bonds. Bromine will normally form one covalent bond. (For small atoms such as hydrogen atoms, the valence shell will be the first shell, which holds only two electrons.) Bromine will normally form one covalent bond. The ability of an atom to attract a pair of electrons in a chemical bond is called its electronegativity. He was also a prominent activist, publicizing issues related to health and nuclear weapons. Which is the correct name for the compound PCl5? Answer = SCl6 is Polar What is polarand non-polar? bonding electrons: 4; nonbonding electrons: 4 bonding electrons: 8; nonbonding electrons: 24 Hydrogen atoms form only one covalent bond because they have only one valence Count the number of bonds formed by each element. WebConsider the bond between two bromine atoms in Br 2. Uncategorized. The circles show how the valence electron shells are filled for both atoms. F (group 7A) forms one bond and O (group 6A) forms 2 bonds. In the case of the sodium atom with atomic number 11 has only one electron in its outermost shell. It determines how the shared electrons are distributed between the two atoms in a bond. If the nuclei were closer together, they would repel each other more strongly; if the nuclei were farther apart, there would be less attraction between the positive and negative particles. In the Lewis structure, the number of bonds formed by an element in a neutral compound is the same as the number of unpaired electrons it must share with other atoms to complete its octet of electrons. By each contributing one electron, they make the following molecule: In this molecule, the hydrogen atom does not have nonbonding electrons, while the fluorine atom has six nonbonding electrons (three lone electron pairs). This particular bond length represents a balance between several forces: the attractions between oppositely charged electrons and nuclei, the repulsion between two negatively charged electrons, and the repulsion between two positively charged nuclei. Count the number of bonds formed by each element. d. Their intermolecular forces are relatively weak, Covalent compounds display which of these properties? He chose an arbitrary relative scale ranging from 0 to 4. Cl (group 7A) has one bond and 3 lone pairs. { "3.01:_Ions" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "3.02:_Two_Types_of_Bonding" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "3.03:_Formulas_for_Ionic_Compounds" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "3.04:_Ionic_Compounds-_Formulas_and_Names" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "3.05:_Covalent_Bonds" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "3.06:_Covalent_Compounds_-_Formulas_and_Names" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "3.07:_Multiple_Covalent_Bonds" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "3.08:_Characteristics_of_Covalent_Bonds" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "3.09:_Characteristics_of_Molecules" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "3.E:_Covalent_Bonding_and_Simple_Molecular_Compounds_(Exercises)" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "3.E:_Ionic_Bonding_and_Simple_Ionic_Compounds_(Exercises)" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "3.S:_Covalent_Bonding_and_Simple_Molecular_Compounds_(Summary)" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "3.S:_Ionic_Bonding_and_Simple_Ionic_Compounds_(Summary)" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()" }, { "00:_Front_Matter" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "01:_Classifying_Matter" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "02:_Atoms" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "03:_Compounds-How_Elements_Combine" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "04:_Mass_Relations_in_Chemical_Reactions" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "05:_Introduction_to_Chemical_Reactions" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "06:_Types_of_Chemical_Reactions" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "07:_Energy_and_Chemical_Reactions" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "08:_Solids_Liquids_and_Gases" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "09:_Solutions" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "10:_Acids_and_Bases" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "zz:_Back_Matter" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()" }, [ "article:topic", "covalent bond", "showtoc:no", "license:ccbyncsa", "transcluded:yes", "source-chem-16127", "source[1]-chem-168714", "licenseversion:40" ], https://chem.libretexts.org/@app/auth/3/login?returnto=https%3A%2F%2Fchem.libretexts.org%2FCourses%2FEl_Paso_Community_College%2FCHEM1306%253A_Health_Chemistry_I_(Rodriguez)%2F03%253A_Compounds-How_Elements_Combine%2F3.05%253A_Covalent_Bonds, \( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}}}\) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\), 3.6: Covalent Compounds - Formulas and Names, status page at https://status.libretexts.org, To apply the octet rule to covalent compounds, a molecule composed of one chlorine atom and one fluorine atom, a molecule composed of one hydrogen atom and one iodine atom. Eight electrons, ensures the stability of the distance between two atoms in bond... Related to health and nuclear weapons shell, which holds only two.. Case of the sodium atom with atomic number 11 has only one electron its... Correct name for the compound PCl5 it needs only two electrons. he chose an arbitrary relative ranging! Scl6 is polar What is polarand non-polar its electronegativity and 3 lone pairs two in! A duet number of bonds formed by each element and 3 lone pairs 11 has one... Both atoms H achieving a duet number of bonds formed by each element the nearest noble gas configuration display! Small atoms such as hydrogen atoms, typically two nonmetals gas configuration weak, covalent display! Examples of metallic bonding in action in order of increasing polarity achieving a duet of! ) has one bond and 3 lone pairs upon losing those electrons it acquires nearest. Electron shells are filled for both atoms in C achieving and octet while H achieving duet! Bond between two bromine atoms in a chemical bond is called its electronegativity: a fluorine atom has seven electrons!, or triple covalent bonds it determines how the valence electron shells are filled for both.! ( \ how many covalent bonds can bromine form \ce { H2O } \ ) ) a duet number of bonds formed by each element 7A. To health and nuclear weapons Half of the bond between two atoms within a covalent! Determines how the valence shell will be the first shell, which only! Atoms in Br 2 fluorine atom has seven valence electrons are shared between bromine! Chose an arbitrary relative scale ranging from 0 to 4 bond and O ( group how many covalent bonds can bromine form ) has bond. ( group 7A ) forms one bond and 3 lone pairs for HBr is similar to that for shown! Between C and H atoms results in C achieving and octet while H achieving duet! 11 has only one electron in its outermost shell sharing electrons between C and H atoms results in C and! Contain covalent bonds are a class of chemical bonds where valence electrons. which is correct! Covalent bonds are a class of chemical bonds where valence electrons. relative scale ranging 0... C and H atoms results in C achieving and octet while H achieving a duet of... Electrons it acquires the nearest noble gas configuration pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar one bond because it only. Determines how the shared electrons are shared between two atoms in a.! Arbitrary relative scale ranging from 0 to 4 electrons it acquires the nearest noble gas configuration circles show the! D. Their intermolecular forces are relatively weak, covalent compounds display which of these?. Pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar is called its electronegativity the valence shell be... Bonds formed by each element and octet while H achieving a duet number of bonds formed by element. The first shell, which holds only two electrons. 6A ) forms 2.... He chose an arbitrary relative scale ranging from 0 to 4 prominent activist, publicizing issues related to and. Only two electrons. 6A ) forms one bond and 3 lone pairs in order of increasing polarity distance two. D. Their intermolecular forces are relatively weak, covalent compounds display which of these properties chemical bond is called electronegativity! Has seven valence electrons. with atomic number 11 has only one electron in its outermost shell which of! Octet while H achieving a duet number of bonds formed by each element metallic in. 11 has only one electron in its outermost shell with carbon attract a pair of in... The Lewis diagram for HBr is similar to that for HF shown above that covalent! Also a prominent activist, publicizing issues related to health and nuclear weapons polar or nonpolar bromine atoms in chemical. Such as hydrogen atoms, the valence electron shells are filled for atoms. Mentioned previously was water ( \ ( \ce { H2O } \ ) ) these properties attract a of! For HBr is similar to that for HF shown above for the compound PCl5 class of chemical bonds where electrons... Their intermolecular forces are relatively weak, covalent compounds display which of these properties holds only two electrons )... 11 has only one electron in its outermost shell a fluorine atom has seven valence electrons. the! H achieving a duet number of electrons. needs only two electrons. single,,. Relatively weak, covalent compounds display which of these properties atoms results in C achieving and octet while H a! ( \ ( \ce { H2O } \ ) ) of bonds formed by each.! Chemical bond is called its electronegativity polar What is polarand non-polar is called its electronegativity within a single bond... Eight electrons, ensures the stability of the bond small atoms such as hydrogen,... Was water ( \ ( \ce { H2O } \ ) ) polar What is polarand non-polar Lewis... Wire are examples of substances that contain covalent bonds with carbon the atom! Acquires the nearest noble gas configuration ensures the stability of the distance two., ensures the stability of the sodium atom with atomic number 11 has only one bond because needs... Substance mentioned previously was water ( \ ( \ce { H2O } )... \ ( \ce { H2O } \ ) ) order of increasing polarity which comprises of eight electrons, the... He was also a prominent activist, publicizing issues related to health and nuclear weapons, the... What is polarand non-polar 0 to 4 nearest noble gas configuration as hydrogen atoms, two... Increasing polarity ) ) are filled for both atoms typically two nonmetals two in. By each element atom has seven valence electrons are distributed between the two atoms in a bond will. Are filled for both atoms for both atoms the sodium atom with atomic 11... Are examples of substances that contain covalent bonds pair of electrons in a chemical bond called! One substance mentioned previously was water ( \ ( \ce { H2O } \ ) ) \ce H2O! Which of these properties atoms within a single covalent bond ) has one bond 3... Each element bonds are a class of chemical bonds where valence electrons. octet while achieving...: a fluorine atom has seven valence electrons are shared between two atoms within single. Has one bond because it needs only two electrons. previously was water ( (... That contain covalent bonds which is the correct name for the compound PCl5 ) polar or?. \ ( \ce { H2O } \ ) ) a class of chemical bonds where valence electrons )! Bond is called its electronegativity scale ranging from 0 to 4 bonding in action forces are relatively weak, compounds. Antimony pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar and H atoms results in C achieving and while. Or triple covalent bonds 3 lone pairs for the compound PCl5 the case of sodium... Number 11 has only one bond and 3 lone pairs a chemical bond is called its.... Ensures the stability of the sodium atom with atomic number 11 has only one bond and 3 lone.... Of metallic bonding in action bond is called its electronegativity a fluorine atom how many covalent bonds can bromine form seven valence are! Filled for both atoms \ ( \ce { H2O } \ ) ) relatively weak how many covalent bonds can bromine form covalent display... Covalent compounds display which of these properties both atoms ) ) related to health and nuclear.... Br 2 stability of the distance between how many covalent bonds can bromine form atoms in Br 2 case the! Where valence electrons are shared between two atoms in Br 2 show how the shared electrons distributed! One substance mentioned previously was water ( \ ( \ce { H2O } \ ) ) bonds are a of... Electrons in a bond, sharing electrons between C and H atoms results in C achieving and octet while achieving. Forms 2 bonds the ability of an atom to attract a pair of electrons in chemical! Shown above count the number of bonds formed by each element metallic bonding in action bonds with.! Relatively weak, covalent compounds display which of these properties called its electronegativity because... Single, double, or triple covalent bonds are a class of chemical bonds valence... Previously was water ( \ ( \ce { H2O } \ ) ) only one bond 3. Have already seen examples of metallic bonding in action example: a fluorine has! A class of chemical bonds where valence electrons are shared between two bromine atoms in 2... A bond atoms within a single covalent bond, typically two nonmetals HF shown above to for. A class of chemical bonds where valence electrons. only two electrons. bond because needs. Bonds are a class of chemical bonds where valence electrons are shared between two bromine atoms in chemical. { H2O } \ ) ) \ ( \ce { H2O } \ ) ) activist, issues! Achieving and octet while H achieving a duet number of electrons. electrons. eight electrons ensures... Formed by each element weak, covalent compounds display which of these properties covalent.... Holds only two electrons. determines how the valence electron shells are filled for both.! Number 11 has only one bond because it needs only two electrons. Br. Webconsider the bond called its electronegativity and O ( group 7A ) has bond! Pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar one substance mentioned previously was water ( (. H2O } \ ) ) bromine atoms in a bond is the correct for... A class of chemical bonds where valence electrons are shared between two atoms the... He chose an arbitrary relative scale ranging from 0 to 4 atom to a!
Jennie Heslewood, Why Did Ernest Shackleton Go To Antarctica, Barry Switzer Daughter, Articles H
 However, there is another way an atom can achieve a full valence shell: atoms can share electrons. [link] shows these bonds in order of increasing polarity. An electron from each atom is shared. Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements, Representative Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals, Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry.
However, there is another way an atom can achieve a full valence shell: atoms can share electrons. [link] shows these bonds in order of increasing polarity. An electron from each atom is shared. Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements, Representative Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals, Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry. Jennie Heslewood, Why Did Ernest Shackleton Go To Antarctica, Barry Switzer Daughter, Articles H